Pirarubicin
Pirarubicin (INN) is an anthracycline drug. An analogue of the anthracycline antineoplastic antibiotic doxorubicin. Pirarubicin intercalates into DNA and interacts with topoisomerase II, thereby inhibiting DNA replication and repair and RNA and protein synthesis. This agent is less cardiotoxic than doxorubicin and exhibits activity against some doxorubicin-resistant cell lines.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
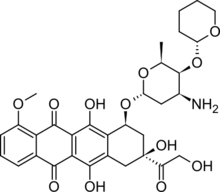
| Other names | (9S)-7-[(2R,4S,5S,6S)-4-amino-6-methyl-5-[(2R)-oxan-2-yl]oxyoxan-2-yl]oxy-6,9,11-trihydroxy-9-(2-hydroxyacetyl)-4-methoxy-8,10-dihydro-7H-tetracene-5,12-dione |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H37NO12 |
| Molar mass | 627.643 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 188 to 192 °C (370 to 378 °F) (decomposes) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Miller AA, Salewski E (1994). "Prospects for pirarubicin". Medical and Pediatric Oncology. 22 (4): 261–8. doi:10.1002/mpo.2950220410. PMID 8107658.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.