Stilbestrol
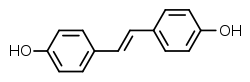
Stilbestrol, or stilboestrol, also known as 4,4'-dihydroxystilbene or 4,4'-stilbenediol, is a stilbenoid nonsteroidal estrogen[1] and the parent compound of a group of more potent nonsteroidal estrogen derivatives that includes, most notably, diethylstilbestrol (DES).[1][2][3] The term "stilbestrol" is often used incorrectly to refer to DES, but they are not the same compound.[2]
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
4,4′-[(E)-Ethene-1,2-diyl]diphenol | |
| Other names
Dihydroxystilbene; 4,4'-Dihydroxystilbene, 4,4'-stilbenediol | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C14H12O2 |
| Molar mass | 212.24388 g/mol |
Magnetic susceptibility (χ) |
-130·10−6 cm3/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Stilbestrol itself is an active estrogen but is less potent than DES and other derivatives.[1]
Stilbestrol derivatives
The stilbestrol estrogenic drugs include the following:
- Acefluranol (an antiestrogen)
- Benzestrol (technically not a stilbestrol derivative due to its elongated central chain, but a very close analogue and grouped with the stilbestrol estrogens in any case)
- Bifluranol
- Dienestrol
- Diethylstilbestrol (commonly, but erroneously shortened to simply “stilbestrol”)
- Diethylstilbestrol diacetate
- Diethylstilbestrol dilaurate
- Diethylstilbestrol dipalmitate
- Diethylstilbestrol dipropionate
- Diethylstilbestrol disulfate
- Diethylstilbestrol monobenzyl ether
- Dimestrol (dianisylhexene, diethylstilbestrol dimethyl ether, dimethoxydiethylstilbene)
- Fosfestrol (diethylstilbestrol diphosphate)
- Furostilbestrol (diethylstilbestrol difuroate)
- ICI-85966 (diethylstilbestrol bis[di(2-chloroethyl)carbamate)
- Mestilbol (diethylstilbestrol monomethyl ether)
- Dimethylstilbestrol
- Hexestrol (dihydrodiethylstilbestrol)
- Diaethiphenum (hexestrol bis(2-diethylaminoethyl) ether) (a coronary vasodilator)
- Hexestrol diacetate
- Hexestrol dicaprylate
- Hexestrol diphosphate
- Hexestrol dipropionate
- Phenestrol (hexestrol bis[4-[bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]phenylacetate)
- Methestrol (promethestrol; dimethylhexestrol)
- Methestrol dipropionate (promethestrol dipropionate)
- Pentafluranol
- Terfluranol
Of the stilbestrol estrogens, diethylstilbestrol, hexestrol, and benzestrol are the most well-known.[4]
Mechanism of action
The stilbestrol estrogens bind with high affinity to both ERα and ERβ.[5]
| Ligand | Other names | Relative binding affinities (RBA, %)a | Absolute binding affinities (Ki, nM)a | Action | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ERα | ERβ | ERα | ERβ | |||
| Estradiol | E2; 17β-Estradiol | 100 | 100 | 0.115 (0.04–0.24) | 0.15 (0.10–2.08) | Estrogen |
| Estrone | E1; 17-Ketoestradiol | 16.39 (0.7–60) | 6.5 (1.36–52) | 0.445 (0.3–1.01) | 1.75 (0.35–9.24) | Estrogen |
| Estriol | E3; 16α-OH-17β-E2 | 12.65 (4.03–56) | 26 (14.0–44.6) | 0.45 (0.35–1.4) | 0.7 (0.63–0.7) | Estrogen |
| Estetrol | E4; 15α,16α-Di-OH-17β-E2 | 4.0 | 3.0 | 4.9 | 19 | Estrogen |
| Alfatradiol | 17α-Estradiol | 20.5 (7–80.1) | 8.195 (2–42) | 0.2–0.52 | 0.43–1.2 | Metabolite |
| 16-Epiestriol | 16β-Hydroxy-17β-estradiol | 7.795 (4.94–63) | 50 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 17-Epiestriol | 16α-Hydroxy-17α-estradiol | 55.45 (29–103) | 79–80 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 16,17-Epiestriol | 16β-Hydroxy-17α-estradiol | 1.0 | 13 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 2-Hydroxyestradiol | 2-OH-E2 | 22 (7–81) | 11–35 | 2.5 | 1.3 | Metabolite |
| 2-Methoxyestradiol | 2-MeO-E2 | 0.0027–2.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 4-Hydroxyestradiol | 4-OH-E2 | 13 (8–70) | 7–56 | 1.0 | 1.9 | Metabolite |
| 4-Methoxyestradiol | 4-MeO-E2 | 2.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 2-Hydroxyestrone | 2-OH-E1 | 2.0–4.0 | 0.2–0.4 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 2-Methoxyestrone | 2-MeO-E1 | <0.001–<1 | <1 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 4-Hydroxyestrone | 4-OH-E1 | 1.0–2.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 4-Methoxyestrone | 4-MeO-E1 | <1 | <1 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 16α-Hydroxyestrone | 16α-OH-E1; 17-Ketoestriol | 2.0–6.5 | 35 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 2-Hydroxyestriol | 2-OH-E3 | 2.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| 4-Methoxyestriol | 4-MeO-E3 | 1.0 | 1.0 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol sulfate | E2S; Estradiol 3-sulfate | <1 | <1 | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol disulfate | Estradiol 3,17β-disulfate | 0.0004 | ? | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol 3-glucuronide | E2-3G | 0.0079 | ? | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol 17β-glucuronide | E2-17G | 0.0015 | ? | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estradiol 3-gluc. 17β-sulfate | E2-3G-17S | 0.0001 | ? | ? | ? | Metabolite |
| Estrone sulfate | E1S; Estrone 3-sulfate | <1 | <1 | >10 | >10 | Metabolite |
| Estradiol benzoate | EB; Estradiol 3-benzoate | 10 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Estradiol 17β-benzoate | E2-17B | 11.3 | 32.6 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Estrone methyl ether | Estrone 3-methyl ether | 0.145 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| ent-Estradiol | 1-Estradiol | 1.31–12.34 | 9.44–80.07 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Equilin | 7-Dehydroestrone | 13 (4.0–28.9) | 13.0–49 | 0.79 | 0.36 | Estrogen |
| Equilenin | 6,8-Didehydroestrone | 2.0–15 | 7.0–20 | 0.64 | 0.62 | Estrogen |
| 17β-Dihydroequilin | 7-Dehydro-17β-estradiol | 7.9–113 | 7.9–108 | 0.09 | 0.17 | Estrogen |
| 17α-Dihydroequilin | 7-Dehydro-17α-estradiol | 18.6 (18–41) | 14–32 | 0.24 | 0.57 | Estrogen |
| 17β-Dihydroequilenin | 6,8-Didehydro-17β-estradiol | 35–68 | 90–100 | 0.15 | 0.20 | Estrogen |
| 17α-Dihydroequilenin | 6,8-Didehydro-17α-estradiol | 20 | 49 | 0.50 | 0.37 | Estrogen |
| Δ8-Estradiol | 8,9-Dehydro-17β-estradiol | 68 | 72 | 0.15 | 0.25 | Estrogen |
| Δ8-Estrone | 8,9-Dehydroestrone | 19 | 32 | 0.52 | 0.57 | Estrogen |
| Ethinylestradiol | EE; 17α-Ethynyl-17β-E2 | 120.9 (68.8–480) | 44.4 (2.0–144) | 0.02–0.05 | 0.29–0.81 | Estrogen |
| Mestranol | EE 3-methyl ether | ? | 2.5 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Moxestrol | RU-2858; 11β-Methoxy-EE | 35–43 | 5–20 | 0.5 | 2.6 | Estrogen |
| Methylestradiol | 17α-Methyl-17β-estradiol | 70 | 44 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Diethylstilbestrol | DES; Stilbestrol | 129.5 (89.1–468) | 219.63 (61.2–295) | 0.04 | 0.05 | Estrogen |
| Hexestrol | Dihydrodiethylstilbestrol | 153.6 (31–302) | 60–234 | 0.06 | 0.06 | Estrogen |
| Dienestrol | Dehydrostilbestrol | 37 (20.4–223) | 56–404 | 0.05 | 0.03 | Estrogen |
| Benzestrol (B2) | – | 114 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Chlorotrianisene | TACE | 1.74 | ? | 15.30 | ? | Estrogen |
| Triphenylethylene | TPE | 0.074 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Triphenylbromoethylene | TPBE | 2.69 | ? | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Tamoxifen | ICI-46,474 | 3 (0.1–47) | 3.33 (0.28–6) | 3.4–9.69 | 2.5 | SERM |
| Afimoxifene | 4-Hydroxytamoxifen; 4-OHT | 100.1 (1.7–257) | 10 (0.98–339) | 2.3 (0.1–3.61) | 0.04–4.8 | SERM |
| Toremifene | 4-Chlorotamoxifen; 4-CT | ? | ? | 7.14–20.3 | 15.4 | SERM |
| Clomifene | MRL-41 | 25 (19.2–37.2) | 12 | 0.9 | 1.2 | SERM |
| Cyclofenil | F-6066; Sexovid | 151–152 | 243 | ? | ? | SERM |
| Nafoxidine | U-11,000A | 30.9–44 | 16 | 0.3 | 0.8 | SERM |
| Raloxifene | – | 41.2 (7.8–69) | 5.34 (0.54–16) | 0.188–0.52 | 20.2 | SERM |
| Arzoxifene | LY-353,381 | ? | ? | 0.179 | ? | SERM |
| Lasofoxifene | CP-336,156 | 10.2–166 | 19.0 | 0.229 | ? | SERM |
| Ormeloxifene | Centchroman | ? | ? | 0.313 | ? | SERM |
| Levormeloxifene | 6720-CDRI; NNC-460,020 | 1.55 | 1.88 | ? | ? | SERM |
| Ospemifene | Deaminohydroxytoremifene | 0.82–2.63 | 0.59–1.22 | ? | ? | SERM |
| Bazedoxifene | – | ? | ? | 0.053 | ? | SERM |
| Etacstil | GW-5638 | 4.30 | 11.5 | ? | ? | SERM |
| ICI-164,384 | – | 63.5 (3.70–97.7) | 166 | 0.2 | 0.08 | Antiestrogen |
| Fulvestrant | ICI-182,780 | 43.5 (9.4–325) | 21.65 (2.05–40.5) | 0.42 | 1.3 | Antiestrogen |
| Propylpyrazoletriol | PPT | 49 (10.0–89.1) | 0.12 | 0.40 | 92.8 | ERα agonist |
| 16α-LE2 | 16α-Lactone-17β-estradiol | 14.6–57 | 0.089 | 0.27 | 131 | ERα agonist |
| 16α-Iodo-E2 | 16α-Iodo-17β-estradiol | 30.2 | 2.30 | ? | ? | ERα agonist |
| Methylpiperidinopyrazole | MPP | 11 | 0.05 | ? | ? | ERα antagonist |
| Diarylpropionitrile | DPN | 0.12–0.25 | 6.6–18 | 32.4 | 1.7 | ERβ agonist |
| 8β-VE2 | 8β-Vinyl-17β-estradiol | 0.35 | 22.0–83 | 12.9 | 0.50 | ERβ agonist |
| Prinaberel | ERB-041; WAY-202,041 | 0.27 | 67–72 | ? | ? | ERβ agonist |
| ERB-196 | WAY-202,196 | ? | 180 | ? | ? | ERβ agonist |
| Erteberel | SERBA-1; LY-500,307 | ? | ? | 2.68 | 0.19 | ERβ agonist |
| SERBA-2 | – | ? | ? | 14.5 | 1.54 | ERβ agonist |
| Coumestrol | – | 9.225 (0.0117–94) | 64.125 (0.41–185) | 0.14–80.0 | 0.07–27.0 | Xenoestrogen |
| Genistein | – | 0.445 (0.0012–16) | 33.42 (0.86–87) | 2.6–126 | 0.3–12.8 | Xenoestrogen |
| Equol | – | 0.2–0.287 | 0.85 (0.10–2.85) | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Daidzein | – | 0.07 (0.0018–9.3) | 0.7865 (0.04–17.1) | 2.0 | 85.3 | Xenoestrogen |
| Biochanin A | – | 0.04 (0.022–0.15) | 0.6225 (0.010–1.2) | 174 | 8.9 | Xenoestrogen |
| Kaempferol | – | 0.07 (0.029–0.10) | 2.2 (0.002–3.00) | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Naringenin | – | 0.0054 (<0.001–0.01) | 0.15 (0.11–0.33) | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| 8-Prenylnaringenin | 8-PN | 4.4 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Quercetin | – | <0.001–0.01 | 0.002–0.040 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Ipriflavone | – | <0.01 | <0.01 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Miroestrol | – | 0.39 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Deoxymiroestrol | – | 2.0 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| β-Sitosterol | – | <0.001–0.0875 | <0.001–0.016 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Resveratrol | – | <0.001–0.0032 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| α-Zearalenol | – | 48 (13–52.5) | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| β-Zearalenol | – | 0.6 (0.032–13) | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Zeranol | α-Zearalanol | 48–111 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Taleranol | β-Zearalanol | 16 (13–17.8) | 14 | 0.8 | 0.9 | Xenoestrogen |
| Zearalenone | ZEN | 7.68 (2.04–28) | 9.45 (2.43–31.5) | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Zearalanone | ZAN | 0.51 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Bisphenol A | BPA | 0.0315 (0.008–1.0) | 0.135 (0.002–4.23) | 195 | 35 | Xenoestrogen |
| Endosulfan | EDS | <0.001–<0.01 | <0.01 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Kepone | Chlordecone | 0.0069–0.2 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| o,p'-DDT | – | 0.0073–0.4 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| p,p'-DDT | – | 0.03 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Methoxychlor | p,p'-Dimethoxy-DDT | 0.01 (<0.001–0.02) | 0.01–0.13 | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| HPTE | Hydroxychlor; p,p'-OH-DDT | 1.2–1.7 | ? | ? | ? | Xenoestrogen |
| Testosterone | T; 4-Androstenolone | <0.0001–<0.01 | <0.002–0.040 | >5000 | >5000 | Androgen |
| Dihydrotestosterone | DHT; 5α-Androstanolone | 0.01 (<0.001–0.05) | 0.0059–0.17 | 221–>5000 | 73–1688 | Androgen |
| Nandrolone | 19-Nortestosterone; 19-NT | 0.01 | 0.23 | 765 | 53 | Androgen |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone | DHEA; Prasterone | 0.038 (<0.001–0.04) | 0.019–0.07 | 245–1053 | 163–515 | Androgen |
| 5-Androstenediol | A5; Androstenediol | 6 | 17 | 3.6 | 0.9 | Androgen |
| 4-Androstenediol | – | 0.5 | 0.6 | 23 | 19 | Androgen |
| 4-Androstenedione | A4; Androstenedione | <0.01 | <0.01 | >10000 | >10000 | Androgen |
| 3α-Androstanediol | 3α-Adiol | 0.07 | 0.3 | 260 | 48 | Androgen |
| 3β-Androstanediol | 3β-Adiol | 3 | 7 | 6 | 2 | Androgen |
| Androstanedione | 5α-Androstanedione | <0.01 | <0.01 | >10000 | >10000 | Androgen |
| Etiocholanedione | 5β-Androstanedione | <0.01 | <0.01 | >10000 | >10000 | Androgen |
| Methyltestosterone | 17α-Methyltestosterone | <0.0001 | ? | ? | ? | Androgen |
| Ethinyl-3α-androstanediol | 17α-Ethynyl-3α-adiol | 4.0 | <0.07 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Ethinyl-3β-androstanediol | 17α-Ethynyl-3β-adiol | 50 | 5.6 | ? | ? | Estrogen |
| Progesterone | P4; 4-Pregnenedione | <0.001–0.6 | <0.001–0.010 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| Norethisterone | NET; 17α-Ethynyl-19-NT | 0.085 (0.0015–<0.1) | 0.1 (0.01–0.3) | 152 | 1084 | Progestogen |
| Norethynodrel | 5(10)-Norethisterone | 0.5 (0.3–0.7) | <0.1–0.22 | 14 | 53 | Progestogen |
| Tibolone | 7α-Methylnorethynodrel | 0.5 (0.45–2.0) | 0.2–0.076 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| Δ4-Tibolone | 7α-Methylnorethisterone | 0.069–<0.1 | 0.027–<0.1 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| 3α-Hydroxytibolone | – | 2.5 (1.06–5.0) | 0.6–0.8 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| 3β-Hydroxytibolone | – | 1.6 (0.75–1.9) | 0.070–0.1 | ? | ? | Progestogen |
| Footnotes: a = (1) Binding affinity values are of the format "median (range)" (# (#–#)), "range" (#–#), or "value" (#) depending on the values available. The full sets of values within the ranges can be found in the Wiki code. (2) Binding affinities were determined via displacement studies in a variety of in-vitro systems with labeled estradiol and human ERα and ERβ proteins (except the ERβ values from Kuiper et al. (1997), which are rat ERβ). Sources: See template page. | ||||||
Closely related compounds
Estrogens closely related to the stilbestrols include paroxypropione (a metabolite of diethylstilbestrol) and the anise and fennel-derived compounds anol, dianol, anethole, dianethole, and photoanethole (from which the stilbestrol estrogens were actually originally derived). The triphenylethylene group of estrogenic drugs that includes triphenylethylene itself, estrobin, chlorotrianisene, broparestrol, ethamoxytriphetol, clomifene, tamoxifen, and more recently developed derivatives is also very closely related structurally to the stilbestrols.
Resveratrol is a stilbenoid with estrogenic properties that is not technically a stilbestrol derivative (it is 3,4',5-stilbenetriol).[6]
Occupational exposure
Occupational exposure to stilbestrol has resulted in gynaecomastia in workers.[7]
See also
References
- Noller KL, Fish CR (July 1974). "Diethylstilbestrol usage: Its interesting past, important present, and questionable future". Med. Clin. North Am. 58 (4): 793–810. doi:10.1016/s0025-7125(16)32122-8. PMID 4276416.
- VITAMINS AND HORMONES. Academic Press. 1 January 1945. pp. 233–. ISBN 978-0-08-086600-0.
- William John Edward Jessop (12 May 2014). Fearon's Introduction to Biochemistry. Elsevier. pp. 408–. ISBN 978-1-4831-9556-8.
- Actions and Uses of Drugs. Stanford University Press. pp. 234–. ISBN 978-0-8047-1505-8.
- Kuiper, George G. J. M.; Carlsson, Bo; Grandien, Kaj; Enmark, Eva; Häggblad, Johan; Nilsson, Stefan; Gustafsson, Jan-Åke (1997). "Comparison of the Ligand Binding Specificity and Transcript Tissue Distribution of Estrogen Receptors α and β". Endocrinology. 138 (3): 863–870. doi:10.1210/endo.138.3.4979. ISSN 0013-7227. PMID 9048584.
- Bhat KP, Lantvit D, Christov K, Mehta RG, Moon RC, Pezzuto JM; Lantvit; Christov; Mehta; Moon; Pezzuto (October 2001). "Estrogenic and antiestrogenic properties of resveratrol in mammary tumor models". Cancer Res. 61 (20): 7456–63. PMID 11606380.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - Fitzsimons, P.M. (October 1944). "Gynaecomastia in Stilboestrol Workers". Br J Ind Med. 1 (4): 235–237. PMC 1035620.