Mobocertinib
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Exkivity |
| Other names | TAK-788, AP-32788 |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Antineoplastic |
| Main uses | Non-small cell lung cancer[1] |
| Side effects | Diarrhea, rash, nausea, inflammation of the mouth, vomiting, decreased appetite, finger nail infections, tiredness, dry skin, musculoskeletal pain[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category | |
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Typical dose | 160 mg OD[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
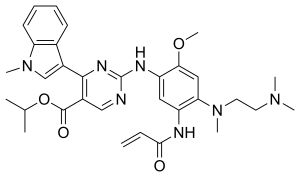
| Formula | C32H39N7O4 |
| Molar mass | 585.709 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Mobocertinib, sold under the brand name Exkivity, is a medication used to treat non-small cell lung cancer.[1] Specifically it is used for advanced cases with an epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutation.[1] It is taken by mouth once per day.[1]
Common side effects include diarrhea, rash, nausea, inflammation of the mouth, vomiting, decreased appetite, finger nail infections, tiredness, dry skin, and musculoskeletal pain.[1] Other side effects may include kidney problems, low potassium, pancreatitis, pneumonitis, and heart problems such as QTc prolongation.[1] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[1] It is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that preferentially inhibits epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) bearing mutations in the exon 20 region.[5]
Mobocertinib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2021.[1] While it is available in the United Kingdom, it is not approved in Europe.[6] In the United Kingdom a month of medication costs the NHS about £7800 as of 2022.[6] In the United States this amount costs 24,600 USD.[7]
Medical uses
Mobocertinib is indicated for adults with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) exon 20 insertion mutations, as detected by an FDA-approved test, whose disease has progressed on or after platinum-based chemotherapy.[4]
Dosage
It is typically used at a dose of 160 mg once per day.[1]
Side Effects
More serious side effects of Mobocertinib may include agitation, bloating of the eyes, lips, feet, blurred vision, coma, decreased urine output, headache, hostility, diarrhea, depression, dizziness, fainting, lethargy, anxiety, nausea, seizures, weight gain, fatigue as well as edema. [8] Other side effects which may be less frequent are: chills, cough, dilated neck veins, ill-feeling and trouble with breathing. [8] Other notable side effects of taking Mobocertinib are: having an acidic stomach, heartburn, acidity, hair loss/thinning, bone pain, sore throat, stuffy nose, trouble swallowing, vomiting and weakness in hands and feet. [8]
Mobocertinib may increase the chance of QTC prolongation, specifically Torsades de Pointes which can be fatal. [8]
Mechanism of action
Mobocertinib acts to inhibit EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations at a lower concentration than it does on wild-type proteins. [9] Mobocertinib is an irreversible kinase inhibitor, forming a covalent bond with the cysteine 797 in the EGFR active site, leading to sustained inhibition of EGFR enzymatic activity. The irreversible binding leads to increased potency via higher affinity binding, more sustained EGFR kinase activity inhibition, and greater overall selectivity, as only a limited number of other kinases possess a cysteine in the equivalent position.[10]
Pharmacokinetics
The volume of distribution of Mobocertinib at steady state is 3,509 L. [9] The mean oral bioavailability of Mobocertinib is 37%. [9] The median Tmax is 4 hours. [9] The average half-life of Mobocertinib and its metabolites is 18 hours. [9] Mobocertinib is metabolized by CYP3A enzymes. [9]
History
Mobocertinib was studied in participants with previously treated metastatic non-small cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 20 insertions.[11][12] It is a first-in-class oral treatment to target EGFR Exon20 insertion mutations.[13]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Exkivity- mobocertinib capsule". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 1 October 2021. Retrieved 30 September 2021.
- 1 2 "Exkivity APMDS". Therapeutic Goods Administration (TGA). 1 August 2022. Archived from the original on 2 August 2022. Retrieved 2 August 2022.
- ↑ "Exkivity 40 mg hard capsules - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 24 March 2022. Archived from the original on 25 March 2022. Retrieved 24 March 2022.
- 1 2 "FDA grants accelerated approval to mobocertinib for metastatic non-sma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 16 September 2021. Archived from the original on 16 September 2021. Retrieved 16 September 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - ↑ "Mobocertinib Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 3 July 2022. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- 1 2 "Mobocertinib". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 28 March 2020. Archived from the original on 11 April 2022. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- ↑ "Exkivity Prices, Coupons, Copay & Patient Assistance". Drugs.com. Retrieved 27 October 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 "Mobocertinib Side Effects: Common, Severe, Long Term". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 3 July 2022. Retrieved 2022-07-03.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Mobocertinib". go.drugbank.com. Archived from the original on 3 July 2022. Retrieved 2022-07-03.
- ↑ Gonzalvez F, Vincent S, Baker TE, Gould AE, Li S, Wardwell SD, et al. (July 2021). "Mobocertinib (TAK-788): A Targeted Inhibitor of EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutants in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer". Cancer Discovery. 11 (7): 1672–1687. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1683. PMID 33632773. S2CID 232056169.
- ↑ Zhou, C; Ramalingam, SS; Kim, TM; Kim, SW; Yang, JC; Riely, GJ; Mekhail, T; Nguyen, D; Garcia Campelo, MR; Felip, E; Vincent, S; Jin, S; Griffin, C; Bunn, V; Lin, J; Lin, HM; Mehta, M; Jänne, PA (1 December 2021). "Treatment Outcomes and Safety of Mobocertinib in Platinum-Pretreated Patients With EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Positive Metastatic Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Phase 1/2 Open-label Nonrandomized Clinical Trial". JAMA Oncology. 7 (12): e214761. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2021.4761. PMC 8517885. PMID 34647988.
- ↑ Riely, GJ; Neal, JW; Camidge, DR; Spira, AI; Piotrowska, Z; Costa, DB; Tsao, AS; Patel, JD; Gadgeel, SM; Bazhenova, L; Zhu, VW; West, HL; Mekhail, T; Gentzler, RD; Nguyen, D; Vincent, S; Zhang, S; Lin, J; Bunn, V; Jin, S; Li, S; Jänne, PA (July 2021). "Activity and Safety of Mobocertinib (TAK-788) in Previously Treated Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with EGFR Exon 20 Insertion Mutations from a Phase I/II Trial". Cancer Discovery. 11 (7): 1688–1699. doi:10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-1598. PMC 8295177. PMID 33632775.
- ↑ "Takeda's Exkivity (mobocertinib) Approved by U.S. FDA as the First Oral Therapy Specifically Designed for Patients with EGFR Exon20 Insertion+ NSCLC" (Press release). Takeda Pharmaceutical Company. 15 September 2021. Archived from the original on 17 September 2021. Retrieved 16 September 2021 – via Business Wire.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
- Clinical trial number NCT02716116 for "A Study of TAK-788 in Adults With Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer" at ClinicalTrials.gov