Bosutinib
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Bosulif |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Tyrosine kinase inhibitor[1] |
| Main uses | Chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML)[2] |
| Side effects | Diarrhea, rash, nausea, tiredness, liver problems, respiratory tract infection, fever, headache[2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | 94–96% |
| Metabolism | By CYP3A4, to inactive metabolites |
| Elimination half-life | 22.5±1.7 hours |
| Excretion | Foecal (91.3%) and renal (3%) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
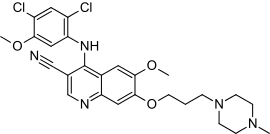
| Formula | C26H29Cl2N5O3 |
| Molar mass | 530.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Bosutinib codenamed SKI-606, marketed under the trade name Bosulif, is a medication used to treat chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).[2] Specifically it is used for cases that are Philadelphia chromosome positive.[2] It is taken by mouth.[2]
Common side effects include diarrhea, rash, nausea, tiredness, liver problems, respiratory tract infection, fever, and headache.[2] Other side effects may include bone marrow suppression, heart damage, swelling, and kidney problems.[2] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[2] It is a tyrosine kinase inhibitor that blocks BCR-ABL and src.[1]
Bosutinib was approved for medical use in the United States in 2012 and Europe in 2013.[2][1] In the United Kingdom 4 weeks of treatment costs the NHS about £3,400 as of 2021.[3] This amount in the United States is about 17,000 USD.[4]
Medical uses
Bosutinib received US FDA and EU European Medicines Agency approval in September 2012, and March 2013, respectively for the treatment of adults with Philadelphia chromosome-positive (Ph+) chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) with resistance, or intolerance to prior therapy.[5][6][7][8]
Dosage
It is generally started at a dose of 400 to 500 mg per day, though may be increased to 600 mg per day.[2]
Contraindications
Bosutinib has two known absolute contraindications, which are: known hypersensitivity to bosutinib and liver impairment.[9][10]
Interactions
Bosutinib is both a substrate and an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and CYP3A4.[11] Hence P-gp and CYP3A4 inhibitors may increase plasma levels of bosutinib.[11] Likewise CYP3A4 inducers may reduce plasma concentrations of bosutinib.[11] It may also alter the metabolism and uptake (into the GIT by means of its P-gp inhibitory effects) of other drugs that are substrates for P-gp and CYP3A4.[11]
Mechanism
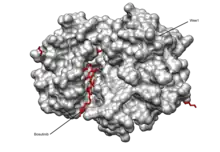
It is an ATP-competitive Bcr-Abl tyrosine-kinase inhibitor with an additional inhibitory effect on Src family kinases (including Src, Lyn and Hck).[11][12] It has also shown activity against the receptors for platelet derived growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor.[13] Bosutinib inhibited 16 of 18 imatinib-resistant forms of Bcr-Abl expressed in murine myeloid cell lines, but did not inhibit T315I and V299L mutant cells.[11]
Bosutinib is metabolized through CYP3A4.
History
References
- 1 2 3 "Bosulif". Archived from the original on 14 November 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 "DailyMed - BOSULIF- bosutinib monohydrate tablet, film coated". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 25 March 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ↑ BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 1015. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Bosulif Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 22 January 2021. Retrieved 11 January 2022.
- ↑ Cortes JE, Kantarjian HM, Brümmendorf TH, Kim DW, Turkina AG, Shen ZX, et al. (October 2011). "Safety and efficacy of bosutinib (SKI-606) in chronic phase Philadelphia chromosome-positive chronic myeloid leukemia patients with resistance or intolerance to imatinib". Blood. 118 (17): 4567–76. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-05-355594. PMC 4916618. PMID 21865346.
- ↑ Cortes JE, Kim DW, Kantarjian HM, Brümmendorf TH, Dyagil I, Griskevicius L, et al. (October 2012). "Bosutinib versus imatinib in newly diagnosed chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: results from the BELA trial". Journal of Clinical Oncology. 30 (28): 3486–92. doi:10.1200/JCO.2011.38.7522. PMC 4979199. PMID 22949154.
- ↑ "Bosulif Approved for Previously Treated Philadelphia Chromosome-Positive Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia". 5 September 2012. Archived from the original on 24 September 2015. Retrieved 1 November 2021.
- ↑ "Bosulif : EPAR - Product Information" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. Pfitzer Ltd. 9 April 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ↑ "Bosulif 100mg and 500mg Tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC)". electronic Medicines Compendium. Pfitzer Limited. 7 June 2013. Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ↑ "BOSULIF (bosutinib monohydrate) tablet, film coated [Pfizer Laboratories Div Pfizer Inc]". DailyMed. Pfitzer Inc. September 2013. Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Bosulif (bosutinib) dosing, indications, interactions, adverse effects, and more". Medscape Reference. WebMD. Archived from the original on 3 January 2014. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
- ↑ Daud AI, Krishnamurthi SS, Saleh MN, Gitlitz BJ, Borad MJ, Gold PJ, et al. (February 2012). "Phase I study of bosutinib, a src/abl tyrosine kinase inhibitor, administered to patients with advanced solid tumors". Clinical Cancer Research. 18 (4): 1092–100. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-2378. PMID 22179664.
- ↑ Bosutinib. livertox.nih.gov. 2012. Archived from the original on 3 April 2018. Retrieved 1 November 2021.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
|