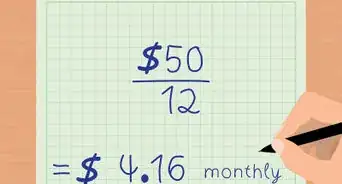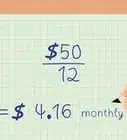This article was co-authored by Michael R. Lewis. Michael R. Lewis is a retired corporate executive, entrepreneur, and investment advisor in Texas. He has over 40 years of experience in business and finance, including as a Vice President for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has a BBA in Industrial Management from the University of Texas at Austin.
There are 7 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page.
This article has been viewed 227,067 times.
Bonds are a kind of debt instrument that offer investors a method of seeing a secure, predictable return.[1] Investors purchase bonds above, below, or at their face value, and then receive coupon payments every six months over the life of the bond, finally receiving the face amount as well when the bond matures. The amount of each coupon payment depends on the terms of the bond, and knowing how to calculate a coupon payment is a matter of performing a simple calculation.
Steps
Gathering the Bond Information
-
1Get the bond's face value. The first piece of information is the actual face value of the bond, sometimes called its par value.[2] Note that this value might be (and probably is) different from what you paid for the bond. It's given to you by your broker.
-
2Locate the bond expiration. You'll also need to locate the bond expiration or maturity date.[3] That way, you can get a sense of how long you'll be receiving coupons and when you can expect to get your money back. This information is also provided to you by your broker.Advertisement
-
3Find the bond coupon rate. The coupon rate is usually expressed as a percentage (e.g., 8%).[4] You'll need this information, also provided by your broker, to calculate the coupon payment.
-
4Get the current yield, if available. The current yield will show you your return on your bond investment, exclusive of capital gains.[5] This value is necessary if you want to calculate your coupon payment based on the price that you're paying for the bond instead of its face value. The current yield may or may not be provided by your broker. If it isn't provided, don't worry about it.
Calculating the Coupon Payment
-
1Use the coupon rate and the face value to calculate the annual payment. If you know the face value of the bond and its coupon rate, you can calculate the annual coupon payment by multiplying the coupon rate times the bond's face value.
- For example, if the coupon rate is 8% and the bond's face value is $1,000, then the annual coupon payment is .08 * 1000 or $80.[6]
-
2Use the current yield to calculate the annual coupon payment. This only works if your broker provided you with the current yield of the bond. To calculate the payment based on the current yield, just multiply the current yield times the amount that you paid for the bond (note, that might not be the same as the bond's face value).
- For example, if you paid $800 for a bond and its current yield is 10%, your coupon payment is .1 * 800 or $80.[7]
-
3Calculate the payment by frequency. Since bondholders generally receive their coupon payments semiannually, you just divide the annual coupon payment by two to receive the actual coupon payment.
- For example, if the annual coupon payment is $80, then the actual coupon payment is $80/2 or $40.
Things You'll Need
- Bond
- Calculator
References
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/b/bond.asp
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/p/parvalue.asp
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/m/maturitydate.asp
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/coupon-rate.asp
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/terms/c/currentyield.asp
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/ask/answers/04/070204.asp
- ↑ http://www.investopedia.com/university/advancedbond/advancedbond3.asp
About This Article
To calculate a coupon payment, multiply the value of the bond by the coupon rate to find out the total annual payment. Alternatively, if your broker told you what the bond yield is, you can multiply this figure by the amount you paid for the bond to work out the annual payment. To calculate the actual coupon payment, divide the annual payment by the frequency of the payment, meaning you would divide it by 2 for semi-annual payments. To find out how to get your bond's maturity date and see some example calculations for coupon payments, keep reading!