This article was co-authored by wikiHow staff writer, Travis Boylls. Travis Boylls is a Technology Writer and Editor for wikiHow. Travis has experience writing technology-related articles, providing software customer service, and in graphic design. He specializes in Windows, macOS, Android, iOS, and Linux platforms. He studied graphic design at Pikes Peak Community College.
This article has been viewed 29,314 times.
Learn more...
Do you need a high-speed USB cable? Are you having a hard time telling if a USB cable you own or are thinking of purchasing supports high-speed data or fast charging? USB cables have gone through a variety of standards over the years. Faster USB standards allow you to transfer data faster as well as charge your phone battery much quicker. This wikiHow article teaches you how to tell if a USB cable is a high-speed USB cable.
Steps
-
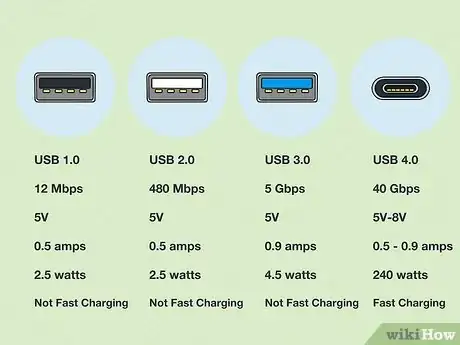
1Understand the different USB standards. Over the years, USB standards have evolved from regular speed to Hi-speed, and now to SuperSpeed. The different USB standards are as follows:[1]
- USB 1.0: This is the oldest USB standard. USB 1.0 cables are capable of data transfer speeds of up to 12 Mbps (Megabytes per second). This is not fast enough to use as a video cable connection. USB 1.0 carries an electrical current of 5 volts (V), 0.5 amps (A), and a max power of 2.5 watts (W), which is not enough power to support fast-charging.
- USB 2.0: USB 2.0 was the first 'hi-speed' USB standard. They are capable of data transfer speeds of up to 480 Mbps. This is faster than USB 1.0, but still not fast enough to use as a video cable connection. USB 2.0 has the same power output as USB 1.0 and does not support fast charging.
- USB 3.0: USB 3.0 is the first "SuperSpeed" USB standard. It is capable of a data transfer speed of up to 5 Gbps (Gigabytes per second) which is fast enough to use as a video cable. Like USB 2.0, they deliver a power output of 5V, but unlike USB 2.0, they can deliver nearly double the watts (4.5W) and amps (0.9A) of a normal USB 2.0 cable. This means it may be able to charge a little faster than a USB 2.0 cable, but is still not considered a fast-charging cable.
- USB 3.1: USB 3.1 is also a "SuperSpeed+" USB standard. USB 3.1 cables are capable of data transfer speeds of up to 10 Gbps and are capable of video transfer. USB 3.1 has a power output of between 5V to 48V, between 0.5A to 0.9A, and up to 240W. These cables are generally considered fast charging cables.
- USB 3.2: USB 3.2 is also a "SuperSpeed+" standard. USB 3.2 is capable of data transfer speeds of up to 20 Gbps. This is fast enough to use as a video cable connection. They have the same power output as a USB 3.1 and are generally considered fast charging cables.
- USB 4.0: USB 4.0 is the latest standard. USB 4.0 is capable of data transfer speeds of up to 40 Gbps. This is more than enough speed to use as a video cable connection. They have the same power output as a USB 3.1 and 3.2, and are generally considered fast charging cables.
-
2Check the male connector. The male connector is the metal plug that plugs into a USB port. There are a variety of male connectors used in USB cables. The following are the different types of USB male connectors:
- USB Type-A: USB Type-A is the most common male connector you will see on a USB cable. They may be used on USB 1.0 up to USB 3.2. They are a rectangle-shaped (12mm x 4.5mm) metal plug. Cables with this type of connector may be capable of fast charging, but they usually aren't as fast as USB Type-C connectors.
- USB Type-B: USB Type-B connectors are somewhat obsolete. They are most commonly used on older PC accessories, like printers. They have an 8mm square-shaped metal plug with notched corners on the top. They can be used with USB 1.0 and 2.0. There is also a USB 3.0 configuration that is a little bit taller (8mm x 10.45mm). These cable types usually aren't capable of fast charging.[2]
- USB Type-C: USB Type-C is one of the newest standards for USB cables. They have a thin, oval-shaped metal connector (8.24mm x 2.4mm). They support all USB standards. Some USB cables have a USB Type-A plug on one end and USB Type-C on the other end. Apple cables may have a USB Type-C on one end, and a Lightning connection type on the other end. These cables are fast, but the fastest cables have a USB Type-C on both ends, or a USB Type-C on one end and a Lightning connection on the other end.
- USB Mini: USB Mini is an older standard that isn't used on as many newer devices. They have a small rectangle-shaped metal plug (6.75mm x 3.0mm) with notched corners on the bottom. USB Mini plugs can be used with USB 1.0 and USB 2.0 cables. They are not capable of fast data transfer or fast charging.
- Micro USB: Micro USB connectors are also rectangle-shaped with notched corners on the bottom. They are much thinner than USB Mini connectors (6.85mm x 1.8mm). They are most commonly used on Android devices that are slightly older. The standard Micro USB connector supports USB 2.0, while the extended 12.25mm x 1.8mm Micro USB plug supports USB 3.0.
- Lightning: Lightning connectors are most commonly used with Apple devices. They support nearly all USB standards and are generally capable of fast charging. They have a square-shaped (6.7mm x 6.7mm) solid metal plug with 8 metal pins on the tip.
- Thunderbolt 3: Thunderbolt 3 cables are also most commonly used with Apple devices. They support all the latest USB standards and are capable of fast charging. They have the exact same plug as USB Type-C. Thunderbolt 3 cables usually have a lightning bolt icon on them.
Advertisement -
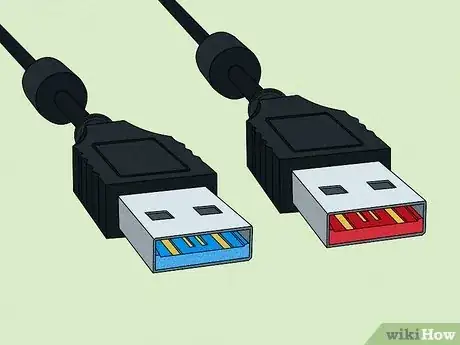
3Check the color inside the USB Type-A plug. Since Type-A connectors are the most common type of USB connectors that are used across a variety of standards, it can be hard to tell what type of USB cable you have. Most USB cable manufacturers use a color-coding system to distinguish which USB standard the cable is using. Check the color of the plastic piece inside the metal plug to see what type of USB cable you are using. The color-coding is as follows:[3]
- White: USB 1.0 (Data speed up to 12 Mbps, power output: 5V, 0.5A, 2.5W).
- Black: USB 2.0 (Data speed up to 480 Mbps, power output: 5V, 0.5A, 2.5W).
- Blue: USB 3.0 (Data speed up to 5 Gbps, power output: 5V, 0.5-0.9A 4.5W).
- Teal: USB 3.1 (Data speed up to 10 Gbps, power output: 5-48V, 0.5-5A, up to 240W).
- Red: USB 3.2 (Data speed up to 20 Gbps, power output: 5-48V, 0.5-5A, up to 240W).
- Yellow: High Power USB 2.0 and 3.0 (fast charging).
- Orange: Charge only USB 3.0
-
4Check the label on the plug. The symbol for USB resembles three wires connected in a fork-like shape. Some cables have a symbol on a USB cable as well as next to USB ports. USB 3.0 and above will usually have the "SS" for SuperSpeed in the USB symbol. They may also have the number "5," "10," "20," or "40" to indicate how many Gbps the cable is capable of transferring.
-
5Check if a USB cable supports a quick charging protocol. There are several quick charging protocols that have been adopted by different brands. The industry standard is USB Power Delivery (USB-PD). Other protocols include Qualcomm Quick Charge (QC), Samsung Adaptive Fast Charging, and Motorola Rapid Charging. These protocols are capable of a power output of at least 60 watts, which means they can quickly charge most cell phones and tablets.
-
6Check the power delivery rating on a quick charging cable. Even if a USB cable supports quick charging, it may not be enough for all devices. A standard USB Type-C to Type-C cable is capable of power delivery of 60 watts. This is enough for most cell phones or tablets. However, a laptop may require more power delivery. For this, you will need a USB cable that has a power delivery rating of 100 watts.[4]
-
7Check the power output of a USB port. It's not just USB cables you need to be worried about. USB ports can also have varying degrees of power output and data transfer rates. USB Type-C ports on a laptop may have varying degrees of data transfer speeds and power delivery. Check the specifications on the device a USB port is connected to see if it's capable of fast charging or fast data transfer.
-
8Check the amperage of the cable. If you still have the package the cable came in, or you are purchasing a cable, check how much amperage the cable supports on the package. A normal USB cable carries about 0.5 amps. A fast-charging USB cable carries at least 2 amps or more.
-
9Check the thickness of the cable. Since fast-charging cables carry a strong electrical current, the wires need to be thicker. If you have nothing else to go by, check the thickness of the cable. If it is thicker than a normal USB cable, it may be a fast charging cable.[5]
References
- ↑ https://uk.rs-online.com/web/generalDisplay.html?id=ideas-and-advice/usb-cable-guide
- ↑ https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/forums/t/659098/usb-cable-wont-work/
- ↑ https://www.tripplite.com/products/usb-connectivity-types-standards
- ↑ https://www.tripplite.com/products/usb-charging
- ↑ https://blog.syncwire.com/how-to-identify-a-fast-charging-cable/
About This Article
1. Check to see if the plastic inside the USB Type-A plug is blue or teal.
2. Check if the USB cable uses a USB Type-C on both ends.
3. Check if the USB cable uses a USB Type-C and a Lightning plug on the other end.
4, Check if a USB cable supports USB-PD, Qualcomm Quick Charge, Samsung Adaptive Fast Charging, or Motorola Rapid Charging.
5. Check if the USB icon on the cable says "SS," "5," "10," "20," or "40."
6. Check the package label to see if the USB cable can carry at least 2 amps.
7. Check if the wires are thicker than normal.
8. Make sure the port the cable is connected to supports fast charging and/or fast data transfer rates.