Quinupristin/dalfopristin
Quinupristin/dalfopristin, or quinupristin-dalfopristin, (pronunciation: kwi NYOO pris tin / dal FOE pris tin) (trade name Synercid) is a combination of two antibiotics used to treat infections by staphylococci and by vancomycin-resistant Enterococcus faecium.
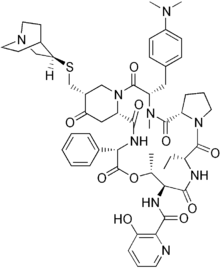 | |
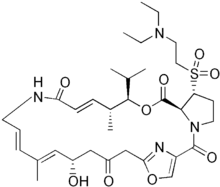 Quinupristin (top) and dalfopristin (bottom) | |
| Combination of | |
|---|---|
| Quinupristin | Streptogramin antibiotic |
| Dalfopristin | Streptogramin antibiotic |
| Clinical data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | IV |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| | |
Quinupristin and dalfopristin are both streptogramin antibiotics, derived from pristinamycin. Quinupristin is derived from pristinamycin IA; dalfopristin from pristinamycin IIA. They are combined in a weight-to-weight ratio of 30% quinupristin to 70% dalfopristin.
Administration
Intravenous, usually 7.5 mg/kg every 8 hours (infections/life threatening VRSA); every 12 hours (skin infections). No renal dosing adjustments, hepatic dosing adjustments are not defined, consider reducing dose.
Mechanism of action
Quinupristin and dalfopristin are protein synthesis inhibitors in a synergistic manner. While each of the two is only a bacteriostatic agent, the combination shows bactericidal activity.
- Dalfopristin binds to the 23S portion of the 50S ribosomal subunit, and changes the conformation of it, enhancing the binding of quinupristin[1] by a factor of about 100. In addition, it inhibits peptidyl transfer.[1]
- Quinupristin binds to a nearby site on the 50S ribosomal subunit and prevents elongation of the polypeptide,[1] as well as causing incomplete chains to be released.[1]
Pharmacokinetics
Clearance by the liver CYP450:3A4 inhibitor, half-life quinupristin 0.8 hours, dalfopristin 0.7 hours (with persistence of effects for 9–10 hours).
Excretion: Quinupristin: 85% feces, 15% urine; Dalfopristin: 81% feces, 19% urine
Side effects
[2]
Serious:
- C.diff-associated diarrhea
- superinfection
- anaphylactoid reactions
- angioedema
Common:
- Joint aches (arthralgia) or muscle aches (myalgia)
- Nausea, diarrhea (C. diff associated) or vomiting
- Rash or itching
- Headache
- Hyperbilirubinemia
- Anemia
- Thrombophlebitis
Drug interactions
The drug inhibits P450 and enhances the effects of terfenadine, astemizole, indinavir, midazolam, calcium channel blockers, warfarin, cisapride and ciclosporin.
References
- Denyer SP, Hodges N, Gorman SP, eds. (2004). Hugo and Russell's Pharmaceutical microbiology (7th ed.). Blackwell Science. p. 212. ISBN 978-0-632-06467-0.
- Epocrates v 19.5
Further reading
- Allington DR, Rivey MP (January 2001). "Quinupristin/dalfopristin: a therapeutic review". Clinical Therapeutics. 23 (1): 24–44. doi:10.1016/S0149-2918(01)80028-X. PMID 11219478.
- Lamb HM, Figgitt DP, Faulds D (December 1999). "Quinupristin/dalfopristin: a review of its use in the management of serious gram-positive infections". Drugs. 58 (6): 1061–97. doi:10.2165/00003495-199958060-00008. PMID 10651391. S2CID 209144323.
- Manzella JP (December 2001). "Quinupristin-dalfopristin: a new antibiotic for severe gram-positive infections". American Family Physician. 64 (11): 1863–6. PMID 11764864..
- Paradisi F, Corti G, Messeri D (January 2001). "Antistaphylococcal (MSSA, MRSA, MSSE, MRSE) antibiotics" (PDF). The Medical Clinics of North America. 85 (1): 1–17. doi:10.1016/s0025-7125(05)70302-3. hdl:2158/329747. PMID 11190346.
- "Synercid". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on 2007-06-18.