Chronic limb threatening ischemia
| Chronic limb threatening ischemia | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Critical limb ischemia, limb threat | |
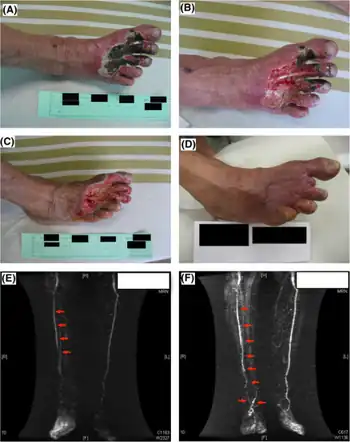 | |
| Critical limb ischemia (cilostazol and clopidogrel combination therapy)-a)Before treatment b)1 week after c) 1 month after d) 90 days after e)magnetic resonance angiography image before treatment f) after 90 days)[1] | |
Chronic limb threatening ischemia (CLTI), also known as critical limb ischemia (CLI), is an advanced stage of peripheral artery disease (PAD). It is defined as ischemic rest pain, arterial insufficiency ulcers, and gangrene. The latter two conditions are jointly referred to as tissue loss, reflecting the development of surface damage to the limb tissue due to the most severe stage of ischemia. Compared to the other manifestation of PAD, intermittent claudication, CLI has a negative prognosis within a year after the initial diagnosis, with 1-year amputation rates of approximately 12% and mortality of 50% at 5 years and 70% at 10 years.[2]
CLI was conceived to identify patients at high-risk for major amputation, but the increasing prevalence of diabetes mellitus has led to a broader conception of limb threat that includes the risk of amputation associated with severely infected and non-healing wounds.[3]
Signs and symptoms
Critical limb ischemia includes rest pain and tissue loss.
Rest pain
Rest pain is a continuous burning pain of the lower leg or feet. It begins, or is aggravated, after reclining or elevating the limb and is relieved by sitting or standing. It is more severe than intermittent claudication, which is also a pain in the legs from arterial insufficiency.
Tissue loss
Tissue loss is the development of arterial insufficiency ulcers or gangrene due to peripheral artery disease.
Diagnosis
Critical limb ischemia is diagnosed by the presence of ischemic rest pain, and an ulcers that will not heal or gangrene due to insufficient blood flow.[4] Insufficient blood flow may be confirmed by ankle-brachial index (ABI), ankle pressure, toe-brachial index (TBI), toe systolic pressure, transcutaneous oxygen measurement (TcPo2 ), or skin perfusion pressure (SPP).[4]
Other factors which may point to a diagnosis of critical limb ischemia are a Buerger's angle of less than 20 degrees during Buerger's test, a capillary refill of more than 15 seconds or diminished or absent pulses.
Critical limb ischemia is different from acute limb ischemia. Acute limb ischemia is a sudden lack of blood flow to the limb, for example caused by an embolus whereas critical limb ischemia is a late sign of a progressive chronic disease.
Treatment
Treatment mirrors that of other symptoms of peripheral artery disease, and includes modifying risk factors, revascularization via vascular bypass or angioplasty, and in the case of tissue loss, wound debridement.
Research
As of 2015 pCMV-vegf165, a gene-therapy was being studied in critical limb ischemia.[5] In 2014, a trial was started to better understand the best revascularization technique for CLI. As of 2017, it had enrolled nearly half of the 2100 people needed to complete the trial.[6] A similar study, BASIL 2 (Bypass Versus Angio plasty in Severe Ischaemia of the Leg), is being conducted in the United Kingdom.[7]
References
- ↑ Spiliopoulos, S. (October 2014). "Antiplatelet therapy in critical limb ischemia: update on clopidogrel and cilostazol". The Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery. 55 (5): 631–640. ISSN 1827-191X. Archived from the original on 14 August 2022. Retrieved 8 August 2022.separate review
- ↑ Varu, Vinit N; Hogg, Melissa E; Kibbe, Melina R (2010). "Critical limb ischemia". Journal of Vascular Surgery. 51 (1): 230–41. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2009.08.073. PMID 20117502.
- ↑ Mills, Joseph L; Conte, Michael S; Armstrong, David G; Pomposelli, Frank B; Schanzer, Andres; Sidawy, Anton N; Andros, George; Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Guidelines Committee (2014). "The Society for Vascular Surgery Lower Extremity Threatened Limb Classification System: Risk stratification based on Wound, Ischemia, and foot Infection (WIfI)". Journal of Vascular Surgery. 59 (1): 220–34.e1–2. doi:10.1016/j.jvs.2013.08.003. PMID 24126108.
- 1 2 Misra, Sanjay; Shishehbor, Mehdi H.; Takahashi, Edwin A.; Aronow, Herbert D.; Brewster, Luke P.; Bunte, Matthew C.; Kim, Esther S.H.; Lindner, Jonathan R.; Rich, Kathleen (12 August 2019). "Perfusion Assessment in Critical Limb Ischemia: Principles for Understanding and the Development of Evidence and Evaluation of Devices: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association". Circulation. 140 (12): e657–e672. doi:10.1161/CIR.0000000000000708. PMC 7372288. PMID 31401843.
- ↑ Deev, Roman V; Bozo, Ilia Y; Mzhavanadze, Nina D; Voronov, Dmitriy A; Gavrilenko, Aleksandr V; Chervyakov, Yuriy V; Staroverov, Ilia N; Kalinin, Roman E; Shvalb, Pavel G; Isaev, Artur A (2015). "PCMV-vegf165 Intramuscular Gene Transfer is an Effective Method of Treatment for Patients with Chronic Lower Limb Ischemia". Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 20 (5): 473–82. doi:10.1177/1074248415574336. PMID 25770117. S2CID 13443907.
- ↑ Menard, Matthew T; Farber, Alik; Assmann, Susan F; Choudhry, Niteesh K; Conte, Michael S; Creager, Mark A; Dake, Michael D; Jaff, Michael R; Kaufman, John A; Powell, Richard J; Reid, Diane M; Siami, Flora Sandra; Sopko, George; White, Christopher J; Rosenfield, Kenneth (2016). "Design and Rationale of the Best Endovascular Versus Best Surgical Therapy for Patients with Critical Limb Ischemia (BEST‐CLI) Trial". Journal of the American Heart Association. 5 (7): e003219. doi:10.1161/JAHA.116.003219. PMC 5015366. PMID 27402237.
- ↑ Popplewell, Matthew A; Davies, Huw; Jarrett, Hugh; Bate, Gareth; Grant, Margaret; Patel, Smitaa; Mehta, Samir; Andronis, Lazaros; Roberts, Tracy; Deeks, Jon; Bradbury, Andrew (2016). "Bypass versus angio plasty in severe ischaemia of the leg - 2 (BASIL-2) trial: Study protocol for a randomised controlled trial". Trials. 17: 11. doi:10.1186/s13063-015-1114-2. PMC 4704263. PMID 26739146.
External links
- Cochrane Peripheral Vascular Diseases Review Group Archived 2015-02-23 at the Wayback Machine