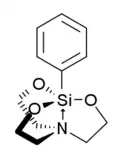
Phenylsilatrane
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
(TBPY-5-23)-8-Phenyltetrahydro-4H-4λ5-8,4-(epoxyethano)[1,3,2]oxazasilolo[3,2-b][1,3,2]oxazasilol-4-ylium-8-uide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.016.603 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C12H17NO3Si |
| Molar mass | 251.357 g·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards |
Toxic |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Phenylsilatrane is a convulsant chemical which has been used as a rodenticide.[1][2] Phenylsilatrane and some of its analogs with 4-substituents of H, CH3, Cl, Br, and CSi(CH3)3 are highly toxic to mice. They have been observed in the laboratory to inhibit the 35S-tert-butylbicyclophosphorothionate (TBPS) binding site (GABA-gated chloride channel) of mouse brain membranes.[3]
See also
- Atrane
- GABAA receptor negative allosteric modulator
- GABAA receptor § Ligands
- Chlorophenylsilatrane
References
- ↑ Voronkov MG (1966). "Silatranes: Intra-Complex Heterocyclic Compounds of Pentacoordinated Silicon" (pdf). Pure and Applied Chemistry. 13 (1–2): 35–60. doi:10.1351/pac196613010035.
- ↑ Lukevics E, Ignatovich L, Khokhlova L, Belyakov S (1997). "Synthesis, Structure, and Toxicity of Arylgermatranes". Chemistry of Heterocyclic Compounds. 33 (2): 239–241. doi:10.1007/BF02256767.
- ↑ Horsham MA, Palmer CJ, Cole LM, Casida JE (1990). "4-Alkynylphenylsilatranes: Insecticidal Activity, Mammalian Toxicity, and Mode of Action". Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 38 (8): 1734–1738. doi:10.1021/jf00098a023.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.