Regadenoson
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Lexiscan, Rapiscan, others |
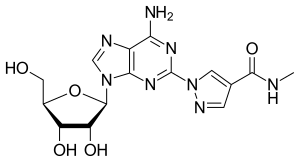
| Other names | CVT-3146, 1-[6-amino-9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]purin-2-yl]- N-methylpyrazole-4-carboxamide |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | A2A adenosine receptor agonist[1] |
| Main uses | Pharmacologic stress testing[2] |
| Side effects | Dizziness, headache, ST segment changes, flushing, shortness of breath, chest pain[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Intravenous |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H18N8O5 |
| Molar mass | 390.360 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Regadenoson, sold under the brand name Lexiscan among others, is a medication used for pharmacologic stress testing.[2] It is used as part of radionuclide myocardial perfusion imaging.[2] It is given by injection into a vein.[2]
Common side effects include dizziness, headache, ST segment changes, flushing, shortness of breath, and chest pain.[1] Other side effects may include seizures and anaphylaxis.[2] It should not be used in people with low blood pressure or poorly controlled heart failure.[1] It is an A2A adenosine receptor agonist which results in vasodilation of blood vessels to the heart. [1]
Regadenoson was approved for medical use in the United States in 2008 and Europe in 2010.[3][1] In the United States it costs about 270 USD per dose as of 2021.[4]
Medical uses
Dosage
It is given at a dose of 0.4 mg.[1]
Chemistry
Regadenoson has a 2 to 3 minute biological half-life, as compared with adenosine's 10-second half-life. As a result, regadenoson stress protocols use a single bolus, instead of a 4-6 minute continuous infusion, which was needed with adenosine. Another difference is that adenosine infusion is weight based (140mcg/kg/minute), while with regadenoson, a 0.4 mg/5mL preloaded syringe dose is standard for all weights. Regadenoson stress tests are not affected by the presence of beta blockers, as regadenoson vasodilates via the adenosine pathway without stimulating beta adrenergic receptors.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Rapiscan EPAR". European Medicines Agency. Archived from the original on 11 August 2020. Retrieved 3 May 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Regadenoson Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 4 March 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ↑ "DailyMed - LEXISCAN- regadenoson injection, solution". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 17 October 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ↑ "Lexiscan Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
|
- "FDA warns of rare but serious risk of heart attack and death with cardiac nuclear stress test drugs Lexiscan (regadenoson) and Adenoscan (adenosine)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 12 January 2017. Archived from the original on 19 September 2020. Retrieved 4 August 2020.