Tolvaptan
-Tolvaptan_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png.webp) | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Samsca, Jinarc, Jynarque, others |
| Other names | OPC-41061 |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Vasopressin-2 receptor (V2) antagonist[1] |
| Main uses | Low sodium, autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)[2][3] |
| Side effects | Thirst, nausea, high sodium, osmotic demyelination syndrome, liver failure, high potassium[1][2] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a609033 |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | Unknown (40% absorbed) |
| Protein binding | 99% |
| Metabolism | Liver (CYP3A4-mediated)[9] |
| Elimination half-life | 12 hours (terminal) |
| Chemical and physical data | |
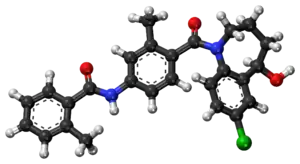
| Formula | C26H25ClN2O3 |
| Molar mass | 448.95 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Tolvaptan, sold under the brand name Samsca among others, is a medication used to treat low sodium due to heart failure or syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH).[2] It is also used for autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).[3] It is taken by mouth.[3] Effects begin within 4 hours.[2]
Common side effects include thirst, nausea, and rapid increase in sodium.[1] Other complications may include osmotic demyelination syndrome, liver failure, and high potassium.[2] It is a vasopressin-2 receptor (V2) antagonist which works by increasing urine production.[1]
Tolvaptan was approved for medical use in the United States and Europe in 2009.[1][2] A generic version was approved in 2020, though was not available commercially as of 2021.[10] In the United States 10 tablets of 30 mg costs about 3,800 USD as of 2021.[11] This amount in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about £750.[3]
Medical uses
Tolvaptan is indicated for the treatment of significant hypervolemic and euvolemic hyponatremia.[12]
Tolvaptan slows kidney function decline in adults at risk of rapidly progressing autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).[13]
Dosage
It is started at 15 mg per day in SIADH.[1] This may be increased to 60 mg per day.[3]
Side effects
The FDA has determined that tolvaptan should not be used for longer than 30 days and should not be used in patients with underlying liver disease because it can cause liver injury, potentially leading to liver failure.[14] When using to treat hyponatremia, it may cause too rapid correction of hyponatremia resulting in osmotic demyelination syndrome.[15]
Pharmacology
Tolvaptan is a selective vasopressin V2 receptor antagonist.[12][13]
Chemistry
Tolvaptan is a racemate, a 1:1 mixture of the following two enantiomers:[16]
| Enantiomers of tolvaptan | |
|---|---|
-Tolvaptan_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png.webp) (R)-Tolvaptan CAS number: 331947-66-1 |
-Tolvaptan_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png.webp) (S)-Tolvaptan CAS number: 331947-44-5 |
History
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted tolvaptan a fast track designation for clinical trials investigating its use for the treatment of polycystic kidney disease.[17] The FDA granted Jynarque an orphan drug designation in April 2012, for the treatment of autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease.[18]
Society and culture
The brand Jynarque, was granted approval for medical use in the United States in April 2018.[19]
Cost
In the United States 10 tablets of 30 mg costs about 3,800 USD as of 2021.[11] This amount in the United Kingdom costs the NHS about £750.[3]
In Ontario Canada in 2013 it was found to be not cost effective at 250 CAD per day and was therefore not covered.[20]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Samsca EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 6 January 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Tolvaptan Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 17 August 2019. Retrieved 8 October 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 BNF (80 ed.). BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 706. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ↑ "Samsca 15 mg tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). Archived from the original on 24 January 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- ↑ "Jinarc 15 mg tablets - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 21 April 2020. Archived from the original on 17 January 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- ↑ "Jynarque- tolvaptan kit Jynarque- tolvaptan tablet". DailyMed. 31 March 2020. Archived from the original on 19 October 2020. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- ↑ "Samsca- tolvaptan tablet". DailyMed. 26 October 2020. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- ↑ "Jinarc EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 7 January 2021. Retrieved 14 December 2020.
- ↑ Shoaf S, Elizari M, Wang Z, et al. (2005). "Tolvaptan administration does not affect steady state amiodarone concentrations in patients with cardiac arrhythmias". J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 10 (3): 165–71. doi:10.1177/107424840501000304. PMID 16211205. S2CID 39158242.
- ↑ "Drugs@FDA: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived from the original on 20 October 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- 1 2 "Tolvaptan Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Retrieved 8 October 2021.
- 1 2 "Samsca- tolvaptan tablet". DailyMed. 28 May 2019. Archived from the original on 18 January 2021. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- 1 2 "Jynarque- tolvaptan kit Jynarque- tolvaptan tablet". DailyMed. 31 March 2020. Archived from the original on 19 October 2020. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ↑ "U.S. Food and Drug Administration." Samsca (Tolvaptan): Drug Safety Communication. N.p., 30 Apr. 2013. Web. 1 June 2014. <http://www.fda.gov/Safety/MedWatch/SafetyInformation/SafetyAlertsforHumanMedicalProducts/ucm350185.htm>
- ↑ Goodman & Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. Brunton, Laurence L, Knollmann, Björn C, Hilal-Dandan, Randa (Thirteenth ed.). New York. ISBN 9781259584732. OCLC 994570810.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ↑ Rote Liste Service GmbH (Hrsg.): Rote Liste 2017 - Arzneimittelverzeichnis für Deutschland (einschließlich EU-Zulassungen und bestimmter Medizinprodukte). Rote Liste Service GmbH, Frankfurt/Main, 2017, Aufl. 57, ISBN 978-3-946057-10-9, S. 222.
- ↑ "Otsuka Maryland Research Institute, Inc. Granted Fast Track Designation For Tolvaptan In PKD". Medical News Today. Healthline Media UK Ltd. Archived from the original on 6 December 2018. Retrieved 6 December 2018.
- ↑ "Tolvaptan Orphan Drug Designations and Approvals". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 6 April 2012. Archived from the original on 29 August 2021. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ↑ "Drug Approval Package: Jynarque (tolvaptan)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 8 June 2018. Archived from the original on 19 March 2021. Retrieved 15 August 2020.
- ↑ "Committee to Evaluate Drugs (CED)" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 12 August 2021. Retrieved 8 October 2021.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |