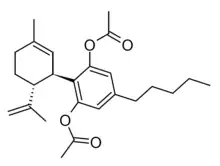
Cannabidiol diacetate
Cannabidiol diacetate (CBD-di-O-Acetate, CBD-DO) is a semi-synthetic derivative of cannabidiol derived by acetylation of the OH groups,[1] which presumably acts as a prodrug for CBD. It has been found as a component of grey-market cannabis products such as e-cigarette liquids and edible gummy lollies.[2]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H34O4 |
| Molar mass | 398.543 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
See also
References
- Appendino G, Gibbons S, Giana A, Pagani A, Grassi G, Stavri M, Smith E, Rahman MM (August 2008). "Antibacterial cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: a structure-activity study". Journal of Natural Products. 71 (8): 1427–30. doi:10.1021/np8002673. PMID 18681481.
- Holt AK, Poklis JL, Peace MR (October 2022). "∆8-THC, THC-O Acetates and CBD-di-O Acetate: Emerging Synthetic Cannabinoids Found in Commercially Sold Plant Material and Gummy Edibles". Journal of Analytical Toxicology. 46 (8): 940–948. doi:10.1093/jat/bkac036. PMC 9564187. PMID 35674405.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.