ACP-105
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
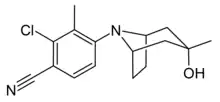
| Formula | C16H19ClN2O |
| Molar mass | 290.79 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
ACP-105 is a drug which acts as a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM). It has been investigated for the treatment of age-related cognitive decline.[1][2][3][4]
See also
References
- ↑ Schlienger N, Lund BW, Pawlas J, Badalassi F, Bertozzi F, Lewinsky R, et al. (November 2009). "Synthesis, structure-activity relationships, and characterization of novel nonsteroidal and selective androgen receptor modulators". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 52 (22): 7186–7191. doi:10.1021/jm901149c. PMID 19856921.
- ↑ Dayger C, Villasana L, Pfankuch T, Davis M, Raber J (March 2011). "Effects of the SARM ACP-105 on rotorod performance and cued fear conditioning in sham-irradiated and irradiated female mice". Brain Research. 1381: 134–140. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.12.088. PMC 3048897. PMID 21219889.
- ↑ George S, Petit GH, Gouras GK, Brundin P, Olsson R (December 2013). "Nonsteroidal selective androgen receptor modulators and selective estrogen receptor β agonists moderate cognitive deficits and amyloid-β levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 4 (12): 1537–1548. doi:10.1021/cn400133s. PMC 3867967. PMID 24020966.
- ↑ Cutler C, Viljanto M, Taylor P, Hincks P, Biddle S, Van Eenoo P (October 2021). "Identification of equine in vitro metabolites of seven non-steroidal selective androgen receptor modulators for doping control purposes". Drug Testing and Analysis. doi:10.1002/dta.3189. PMID 34714606. S2CID 240152623.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.