LG121071
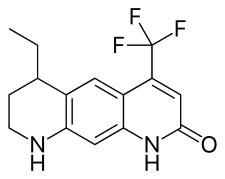 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LG-121071; LGD-121071 |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H15F3N2O |
| Molar mass | 296.293 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
LG121071 (or LGD-121071) is a selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) developed by Ligand Pharmaceuticals that was first described in 1999 and was the first orally active nonsteroidal androgen to be discovered.[1][2] It is a tricyclic quinolone derivative, structurally distinct from other nonsteroidal AR agonists like andarine and enobosarm (ostarine).[2] The drug acts as a high-affinity full agonist of the androgen receptor (AR) (Ki = 17 nM),[2] with a potency and efficacy that is said to be equivalent to that of dihydrotestosterone (DHT).[3] Unlike testosterone, but similarly to DHT, LG121071 and other nonsteroidal androgens cannot be potentiated by 5α-reductase in androgenic tissues (nor aromatized into estrogenic metabolites), and for this reason, show tissue-selective androgenic effects.[4] In accordance, they are said to possess full anabolic activity with reduced androgenic activity, similarly to anabolic-androgenic steroids.[5]
The in vitro metabolism of LG121071 has been characterized in anticipation of its possible use as a doping agent.[5][6]
See also
References
- ↑ Hamann, Lawrence G.; Mani, Neelakandha S.; Davis, Robert L.; Wang, Xiao-Ning; Marschke, Keith B.; Jones, Todd K. (1999). "Discovery of a Potent, Orally Active, Nonsteroidal Androgen Receptor Agonist: 4-Ethyl-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6- (trifluoromethyl)-8-pyridono[5,6-g]- quinoline (LG121071)". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 42 (2): 210–212. doi:10.1021/jm9806648. ISSN 0022-2623. PMID 9925725.
- 1 2 3 Gao, Wenqing; Kim, Juhyun; Dalton, James T. (2006). "Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Nonsteroidal Androgen Receptor Ligands". Pharmaceutical Research. 23 (8): 1641–1658. doi:10.1007/s11095-006-9024-3. ISSN 0724-8741. PMC 2072875. PMID 16841196.
- ↑ Chengalvala, Murty; Oh, Thomas; Roy, Arun K (2005). "Selective androgen receptor modulators". Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 13 (1): 59–66. doi:10.1517/13543776.13.1.59. ISSN 1354-3776.
- ↑ Elbers JM, Grootenhuis AJ (2003). "New tissue-selective androgens: perspectives in the treatment of androgen deficits". Ann. Endocrinol. Paris. 64 (2): 183–8. PMID 12773961.
- 1 2 Knoop, Andre; Krug, Oliver; Vincenti, Marco; Schänzer, Wilhelm; Thevis, Mario (2015). "In vitro metabolism studies on the selective androgen receptor modulator (SARM) LG121071 and its implementation into human doping controls using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry". European Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 21 (1): 27–36. doi:10.1255/ejms.1328. ISSN 1356-1049. PMID 25906032. S2CID 29918434.
- ↑ Gerace, E.; Salomone, A.; Fasano, F.; Costa, R.; Boschi, D.; Di Stilo, A.; Vincenti, M. (2010). "Validation of a GC/MS method for the detection of two quinolinone-derived selective androgen receptor modulators in doping control analysis". Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 400 (1): 137–144. doi:10.1007/s00216-010-4569-8. hdl:2318/86557. ISSN 1618-2642. PMID 21165606. S2CID 43268790.