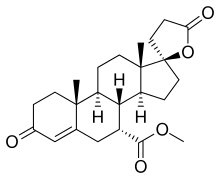
Mexrenone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ZK-32055; SC-25152; 7α-(Methoxycarbonyl)canrenone; 17β-Hydroxy-3-oxo-17α-pregn-4-ene-7α,21-dicarboxylic acid γ-lactone methyl ester |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H32O5 |
| Molar mass | 400.515 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Mexrenone (code names ZK-32055, SC-25152) is a steroidal antimineralocorticoid of the spirolactone group related to spironolactone that was never marketed.[1][2] It is the lactonic form of mexrenoic acid (mexrenoate), and mexrenoate potassium (SC-26714), the potassium salt of mexrenoic acid, also exists.[3] In addition to the mineralocorticoid receptor, mexrenone also binds to the glucocorticoid, androgen, and progesterone receptors.[4] Relative to spironolactone, it has markedly reduced antiandrogen activity (approximately one-tenth of the antimineralocorticoid dosage equivalent antiandrogen activity of spironolactone).[2] Eplerenone is the 9-11α-epoxy analogue of mexrenone.[5]
See also
References
- ↑ Cutler, Gordon B.; Pita, Julio C.; Rifka, Safa M.; Menard, Raymond H.; Sauer, Mark A.; Loriaux, D. Lynn (1978). "SC 25152: A Potent Mineralocorticoid Antagonist with Reduced Affinity for the 5α-Dihydrotestosterone Receptor of Human and Rat Prostate". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 47 (1): 171–175. doi:10.1210/jcem-47-1-171. ISSN 0021-972X. PMID 263288.
- 1 2 Cutler GB, Sauer MA, Loriaux DL (1979). "SC 25152: a potent mineralocorticoid antagonist with decreased antiandrogenic activity relative to spironolactone". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 209 (1): 144–6. PMID 430374.
- ↑ Hofmann LM, Weier RM, Suleymanov OD, Pedrera HA (1977). "Mexrenoate potassium: a steroidal aldosterone antagonist and antihypertensive". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 201 (3): 762–8. PMID 864608.
- ↑ Gyorgy Szasz; Zsuzsanna Budvari-Barany (19 December 1990). Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Antihypertensive Agents. CRC Press. pp. 87–. ISBN 978-0-8493-4724-5.
- ↑ Ménard, Joël (2004). "The 45-year story of the development of an anti-aldosterone more specific than spironolactone". Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology. 217 (1–2): 45–52. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2003.10.008. ISSN 0303-7207. PMID 15134800. S2CID 19701784.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.