Microsporidiosis
| Microsporidiosis | |
|---|---|
| Specialty | Infectious disease |
Microsporidiosis is an opportunistic intestinal infection that causes diarrhea and wasting in immunocompromised individuals (HIV, for example). It results from different species of microsporidia, a group of microbial (unicellular) fungi.[1]
In HIV infected individuals, microsporidiosis generally occurs when CD4+ T cell counts fall below 150.
Microsporidia have emerged with significant mortality risk in immunocompromised individuals. These are small, single-celled, obligately intracellular parasites linked to water sources as well as wild, and domestic animals.[2] They were once considered protozoans or protists, but are now known to be fungi,[3] or a sister group to fungi.[4] The most common causes of microsporidiosis is Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Encephalitozoon intestinalis.
Signs and symptoms
The clinical presentation of this infection is as follows:[5]
- Diarrhea
- Encephalitis
- Ocular infection
- Sinusitis
- Myositis
Cause
At least 15 microsporidian species have been recognized[6] as human pathogens, spread across nine genera:
- Anncaliia
- A. algerae, A. connori, A. vesicularum
- Encephalitozoon
- E. cuniculi, E. hellem, E. intestinalis
- Enterocytozoon
- E. bieneusi
- Microsporidium
- M. ceylonensis, M. africanum
- Nosema
- N. ocularum
- Pleistophora sp.
- Trachipleistophora
- T. hominis, T. anthropophthera
- Vittaforma
- V. corneae.
- Tubulinosema
- T. acridophagus
The primary causes are Enterocytozoon bieneusi and Encephalitozoon intestinalis.[7]
Life cycle
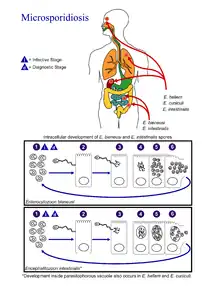
(Coded to image at right).
- The infective form of microsporidia is the resistant spore and it can survive for an extended period of time in the environment.
- The spore extrudes its polar tubule and infects the host cell.
- The spore injects the infective sporoplasm into the eukaryotic host cell through the polar tubule.
- Inside the cell, the sporoplasm undergoes extensive multiplication either by merogony (binary fission) or schizogony (multiple fission).
- This development can occur either in direct contact with the host cell cytoplasm (E. bieneusi) or inside a vacuole called a parasitophorous vacuole (E. intestinalis). Either free in the cytoplasm or inside a parasitophorous vacuole, microsporidia develop by sporogony to mature spores.
- During sporogony, a thick wall is formed around the spore, which provides resistance to adverse environmental conditions. When the spores increase in number and completely fill the host cell cytoplasm, the cell membrane is disrupted and releases the spores to the surroundings.
- These free mature spores can infect new cells thus continuing the cycle.
Diagnosis
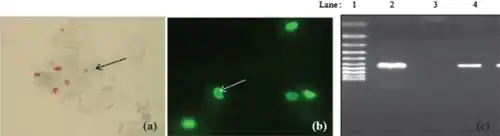
The best option for diagnosis is using PCR.
Diagnosis with Microsporidia can be done through gram-positive, acid-fast spores in stool and biopsy material with morphologic demonstration of the organism. Initial detection through light microscopic examination of tissue sections, stools, duodenal aspirates, nasal discharges, bronchoalveolar lavage fluids, and conjunctival smears.[8] Definitive diagnosis can also be achieved through fluorescein-tagged antibody immunofluorescence or electron microscopy,[8] and species identification can be done through PCR.[9]
Classification
Although it is classified as a protozoal disease in ICD-10, their phylogenetic placement has been resolved to be within the Fungi, and some sources classify microsporidiosis as a mycosis,[10] however, they are highly divergent and rapidly evolving.[11][12][13]
Treatment
Fumagillin has been used in the treatment.[7][14] Another agent used is albendazole.[15]
Because of its severe mortality risk in immunocompromised individuals, two main agents are used: Albendazole, which inhibits tubulin, and Fumagillin, which inhibits methionine aminopeptidase type two.[16]
References
- ↑ "Microsporidiosis: Parasitic Infections: Merck Manual Home Health Handbook". Archived from the original on 2015-02-21. Retrieved 2021-09-25.
- ↑ Didier ES, Maddry JA, Brindley PJ, Stovall ME, Didier PJ. Therapeutic strategies for human microsporidia infections. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2005 Jun;3(3):419-34. doi: 10.1586/14787210.3.3.419. PMID: 15954858.
- ↑ Hibbett, D.S.; et al. (2007). "A higher level phylogenetic classification of the Fungi" (PDF). Mycological Research. 111 (5): 509–47. doi:10.1016/j.mycres.2007.03.004. PMID 17572334. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-10-20. Retrieved 2021-09-25.
- ↑ Silar, Philippe (2016). Protistes Eucaryotes : Origine, Evolution et Biologie des Microbes Eucaryotes. HAL. p. 462. ISBN 978-2-9555841-0-1. Archived from the original on 2019-07-02. Retrieved 2021-09-25.
- ↑ "Microsporidiosis | NIH". clinicalinfo.hiv.gov. Archived from the original on 20 May 2021. Retrieved 23 December 2021.
- ↑ "CDC - DPDx - Microsporidiosis". www.cdc.gov. 2017-12-29. Archived from the original on 2021-06-05. Retrieved 2018-01-04.
- 1 2 Lanternier F, Boutboul D, Menotti J, et al. (February 2009). "Microsporidiosis in solid organ transplant recipients: two Enterocytozoon bieneusi cases and review". Transpl Infect Dis. 11 (1): 83–8. doi:10.1111/j.1399-3062.2008.00347.x. PMID 18803616.
- 1 2 Weber R, Bryan RT, Schwartz DA, Owen RL. Human microsporidial infections. Clin Microbiol Rev. 1994 Oct;7(4):426-61. doi: 10.1128/cmr.7.4.426. PMID: 7834600; PMCID: PMC358336.
- ↑ Kock NP, Petersen H, Fenner T, Sobottka I, Schmetz C, Deplazes P, Pieniazek NJ, Albrecht H, Schottelius J. Species-specific identification of microsporidia in stool and intestinal biopsy specimens by the polymerase chain reaction. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 1997 May;16(5):369-76. doi: 10.1007/BF01726365. PMID: 9228477.
- ↑ Microsporidiosis at the US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- ↑ Didier ES (April 2005). "Microsporidiosis: an emerging and opportunistic infection in humans and animals". Acta Trop. 94 (1): 61–76. doi:10.1016/j.actatropica.2005.01.010. PMID 15777637.
- ↑ Keeling PJ, Luker MA, Palmer JD (January 2000). "Evidence from beta-tubulin phylogeny that microsporidia evolved from within the fungi". Mol. Biol. Evol. 17 (1): 23–31. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a026235. PMID 10666703.
- ↑ Keeling PJ; Madhani, Hiten D. (September 2009). Madhani, Hiten D. (ed.). "Five Questions about Microsporidia". PLOS Pathogens. 5 (9): e1000489. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1000489. PMC 2742732. PMID 19779558.
- ↑ Molina JM, Tourneur M, Sarfati C, et al. (June 2002). "Fumagillin treatment of intestinal microsporidiosis". N. Engl. J. Med. 346 (25): 1963–9. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa012924. PMID 12075057.
- ↑ Didier ES, Maddry JA, Brindley PJ, Stovall ME, Didier PJ (June 2005). "Therapeutic strategies for human microsporidia infections". Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 3 (3): 419–34. doi:10.1586/14787210.3.3.419. PMID 15954858.
- ↑ Han B, Weiss LM. Therapeutic targets for the treatment of microsporidiosis in humans. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2018 Nov;22(11):903-915. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2018.1538360. Epub 2018 Nov 1. PMID: 30336698; PMCID: PMC6300147.
External links
- CDC's microsporidiosis info page.
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |