SARS-CoV-2 Iota variant
| Part of a series on the |
| COVID-19 pandemic |
|---|
 Scientifically accurate atomic model of the external structure of SARS-CoV-2. Each "ball" is an atom. |
|
|
|
Iota variant,[1] also known as lineage B.1.526, is one of the variants of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19. It was first detected in New York City in November 2020. The variant has appeared with two notable mutations: the E484K spike mutation, which may help the virus evade antibodies, and the S477N mutation, which may help the virus bind more tightly to human cells.
By February 2021, it had spread rapidly in the New York region and accounted for about one in four viral sequences.[2][3] By 11 April 2021, the variant had been detected in at least 48 U.S. states and 18 countries.[4][5]
Under the simplified naming scheme proposed by the World Health Organization, B.1.526 has been labeled Iota variant, and is considered a variant of interest (VOI), but not yet a variant of concern.[6]
Mutations
The Iota (B.1.526) genome contains the following amino-acid mutations, all of which are in the virus's spike protein code: L5F, T95I, D253G, E484K, D614G and A701V.[7]
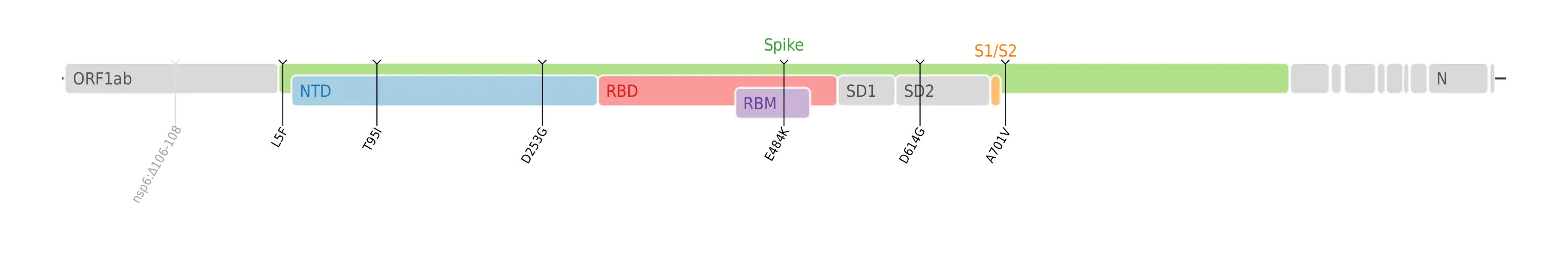 Amino acid mutations of SARS-CoV-2 Iota variant plotted on a genome map of SARS-CoV-2 with a focus on the spike.[8]
Amino acid mutations of SARS-CoV-2 Iota variant plotted on a genome map of SARS-CoV-2 with a focus on the spike.[8]
History
The increase of the Iota variant was captured by researchers at Caltech by scanning for mutations in a database known as GISAID, a global science initiative that has documented over 700,000 genomic sequences of SARS-CoV-2.[9][10]
The proportion of USA cases represented by the Iota variant had declined sharply by the end of July 2021 as the Delta variant became dominant.[11]
Statistics
| Country | Confirmed cases | Last Reported Case |
|---|---|---|
| 45,558 | 24 June 2021 | |
| 168 | 10 June 2021 | |
| 158 | ||
| 119 | 17 June 2021 | |
| 115 | 24 May 2021 | |
| 103 | 10 June 2021 | |
| 56 | 22 June 2021 | |
| 50 | 11 June 2021 | |
| 43 | 16 May 2021 | |
| 17 | 27 May 2021 | |
| 13 | 7 May 2021 | |
| 12 | 17 May 2021 | |
| 11 | 12 May 2021 | |
| 9 | 31 May 2021 | |
| 9 | 26 April 2021 | |
| 9 | 10 May 2021 | |
| 8 | 26 April 2021 | |
| 8 | 18 April 2021 | |
| 8 | 10 June 2021 | |
| 8 | 25 May 2021 | |
| 8 | 28 May 2021 | |
| 7 | 4 April 2021 | |
| 6 | 21 May 2021 | |
| 6 | 4 May 2021 | |
| 6 | 05 March 2021 | |
| 5 | 21 May 2021 | |
| 5 | 19 April 2021 | |
| 5 | 4 June 2021 | |
| 4 | 9 February 2021 | |
| 4 | 7 May 2021 | |
| 4 | 14 April 2021 | |
| 4 | 14 May 2021 | |
| 4 | 4 May 2021 | |
| 4 | 21 December 2020 | |
| 3 | 24 March 2021 | |
| 3 | 15 January 2021 | |
| 3 | 18 May 2021 | |
| 2 | 22 April 2021 | |
| 2 | 20 March 2021 | |
| 2 | 17 January 2021 | |
| 2 | 8 January 2021 | |
| 2 | 2 February 2021 | |
| 2 | 14 May 2021 | |
| 2 | 4 March 2021 | |
| 2 | 17 April 2021 | |
| 1 | 21 April 2021 | |
| 1 | 3 May 2021 | |
| 1 | 25 January 2021 | |
| 1 | 15 April 2021 | |
| 1 | ||
| 1 | 30 April 2021 | |
| 1 | 14 March 2021 | |
| 1 | 9 March 2021 | |
| 1 | 16 March 2021 | |
| 1 | 31 March 2021 | |
| 1 | 22 March 2021 | |
| 1 | 8 May 2021 | |
| World (57 countries) | Total: 46,589 | Total as of 11 August 2021 |
See also
References
- ↑ "Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants". www.who.int. Retrieved June 1, 2021.
- ↑ Rosa-Aquino, Matt Stieb, Paola (March 21, 2021). "Everything We Know About the Coronavirus Variant Spreading in New York City". Intelligencer. Retrieved April 10, 2021.
- ↑ Mandavilli, Apoorva (February 24, 2021). "A New Coronavirus Variant Is Spreading in New York, Researchers Report". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved April 10, 2021.
- ↑ "outbreak.info". outbreak.info. Retrieved April 10, 2021.
- ↑ "PANGO lineages Lineage B.1.526". cov-lineages.org. April 22, 2021. Retrieved April 22, 2021.
- ↑ "Tracking SARS-CoV-2 variants". www.who.int. Retrieved June 1, 2021.
- ↑ "SARS-CoV-2 Variant Classifications and Definitions". CDC.gov. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Retrieved July 5, 2021.
- ↑ "Spike Variants: Iota variant, aka B.1.526". covdb.stanford.edu. Stanford University Coronavirus Antiviral & Resistance Database. July 1, 2021. Retrieved July 5, 2021.
- ↑ Corum, Jonathan; Zimmer, Carl. "Coronavirus Variants and Mutations". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved April 10, 2021.
- ↑ West, Anthony P.; Barnes, Christopher O.; Yang, Zhi; Bjorkman, Pamela J. (February 23, 2021). "SARS-CoV-2 lineage B.1.526 emerging in the New York region detected by software utility created to query the spike mutational landscape". bioRxiv: 2021.02.14.431043. doi:10.1101/2021.02.14.431043. PMC 8077570. PMID 33907745. S2CID 231981267.
- ↑ SARS-CoV-2 sequences by variant, Jul 26, 2021, USA Our World in Data
- ↑ "GISAID - hCov19 Variants". www.gisaid.org. Retrieved July 2, 2021.