Sarecycline
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | sar"e sye' kleen |
| Trade names | Seysara |
| Other names | P-005672 |
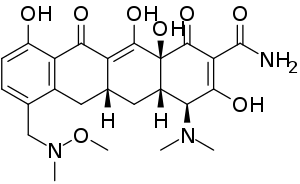
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Tetracycline[1] |
| Main uses | Acne[1] |
| Side effects | Nausea, sunburns, dizziness, Clostridium difficile infection[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Typical dose | 60 to 150 mg OD[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a618068 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C24H29N3O8 |
| Molar mass | 487.509 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Sarecycline is an antibiotic used to treat acne.[1] Specifically it is used for moderate to severe acne of the non-nodular type.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include nausea.[1] Other side effects may include sunburns, dizziness, Clostridium difficile infections.[1] Use during pregnancy may harm the baby.[1] It is in the tetracycline class.[1]
Sarecycline was approved for medical use in the United States in 2018.[2] In the United States it costs about 750 USD per month as of 2021.[3] It is not available in Europe or the United Kingdom as of 2021.[4]
Medical uses
The spectrum of activity is limited to clinically relevant Gram-positive bacteria, mainly Cutibacterium acnes, with little or no activity against Gram-negative bacterial microflora commonly found in the human gastrointestinal tract.[5] Sarecycline has not been tested in spirochetes.
Dosage
It is taken at a dose of 60 to 150 mg once per day depending on a person's weight.[1]
Chemistry
Unlike other tetracycline-class antibiotics, sarecycline has a long C7 moiety that extends into and directly interact with the bacterial messenger RNA (mRNA).[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 "Sarecycline Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 21 January 2021. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ↑ "FDA-approved Labeling-Package Insert for Seysara" (PDF). Drugs@FDA. June 2020. Archived (PDF) from the original on June 7, 2020. Retrieved September 5, 2020.
- ↑ "Seysara Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ↑ "Sarecycline". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 30 March 2017. Archived from the original on 11 October 2021. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ↑ Zhanel, George; Critchley, Ian; Lin, Lynn-Yao; Alvandi, Nancy (2019-01-01). "Microbiological Profile of Sarecycline, a Novel Targeted Spectrum Tetracycline for the Treatment of Acne Vulgaris". Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy. 63 (1). doi:10.1128/AAC.01297-18. ISSN 0066-4804. PMC 6325184. PMID 30397052.
- ↑ Batool, Zahra; Lomakin, Ivan B.; Polikanov, Yury S.; Bunick, Christopher G. (2020-08-25). "Sarecycline interferes with tRNA accommodation and tethers mRNA to the 70S ribosome". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 117 (34): 20530–20537. doi:10.1073/pnas.2008671117. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 7456112. PMID 32817463.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |