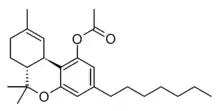
THCP-O-acetate
THCP-O-acetate (THCP-O) is a semi-synthetic derivative of tetrahydrocannabiphorol (THCP) derived by acetylation of the OH group. It has been found as a component of grey-market cannabis products such as e-cigarette liquids and edible gummy lollies, and is allegedly a potent and long-lasting psychoactive cannabinoid.[1]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H36O3 |
| Molar mass | 384.560 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Toxicity
In 2022, researchers at Portland State University who screened for the presence of reacted ketene as N-benzylacetamide reported that Vitamin E acetate, CBD-acetate, CBN-acetate and THC-O-acetate may break down to release ketene gas when heated at 340 °C (644 °F).
The lowest concentration of inhaled ketene that produces a physiologically negative response is 5 ppm (5 parts per million).[2] For this reason it is advised to exercise caution around THC-O acetate and other acetate esters of inhaled drugs.
See also
References
- Erickson BE (2023). "Waiting for CBD regulations in the US". Chemical & Engineering News. 101 (28): 17–19. doi:10.1021/cen-10128-feature1. S2CID 261318144.
- Ketene. National Academies Press (US). 21 March 2014.