Amorolfine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Chemical and physical data | |
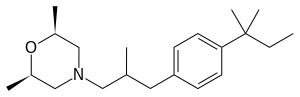
| Formula | C21H35NO |
| Molar mass | 317.517 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Amorolfine (or amorolfin), is a morpholine antifungal drug that inhibits Δ14-sterol reductase and cholestenol Δ-isomerase, which depletes ergosterol and causes ignosterol to accumulate in the fungal cytoplasmic cell membranes. Marketed as Curanail, Loceryl, Locetar, and Odenil, amorolfine is commonly available in the form of a nail lacquer, containing 5% amorolfine hydrochloride as the active ingredient. It is used to treat onychomycosis (fungal infection of the toe- and fingernails). Amorolfine 5% nail lacquer in once-weekly or twice-weekly applications has been shown in two studies to be between 60% and 71% effective in treating toenail onychomycosis; complete cure rates three months after stopping treatment (after six months of treatment) were 38% and 46%. However, full experimental details of these trials were not available and since they were first reported in 1992 there have been no subsequent trials.[1]
It is a topical solution for the treatment of toenail infections.[2][3] Systemic treatments may be considered more effective.[1]
It is approved for sale over-the-counter in Australia, Brazil, Russia, Germany and the UK, and is approved for the treatment of toenail fungus by prescription in other countries. It is not approved for the treatment of onychomycosis in the United States or Canada, but can be ordered from there by mail from other countries.[4]
Notes
- 1 2 Williams HC (2003). Evidence-Based Dermatology. Blackwell. ISBN 9781444300178. Archived from the original on 2021-10-15. Retrieved 2021-05-19.
- ↑ Flagothier C, Piérard-Franchimont C, Piérard GE (March 2005). "New insights into the effect of amorolfine nail lacquer". Mycoses. 48 (2): 91–4. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0507.2004.01090.x. PMID 15743424. Archived from the original on 2020-06-25. Retrieved 2021-05-19.
- ↑ Feng X, Xiong X, Ran Y (May 2017). "Efficacy and tolerability of amorolfine 5% nail lacquer in combination with systemic antifungal agents for onychomycosis: A meta-analysis and systematic review". Dermatologic Therapy. 30 (3): e12457. doi:10.1111/dth.12457. PMID 28097731.
- ↑ It can readily be verified that Curanail is advertised on websites such as US Amazon.com, shipped from abroad.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|