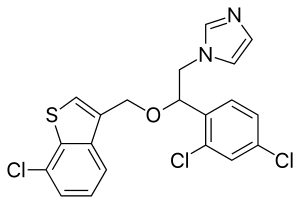
Sertaconazole
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ertaczo, Dermofix, Zalain |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Azole[1] |
| Main uses | Athlete's foot, ringworm, pityriasis versicolor, candidiasis[1] |
| Side effects | Dry skin, burning skin, inflamed skin[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Topical |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a608047 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | Negligible |
| Protein binding | >99% to plasma |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H15Cl3N2OS |
| Molar mass | 437.76 g·mol−1 |
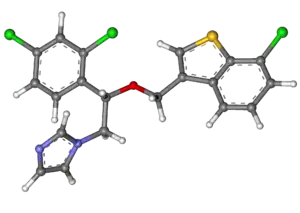
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Sertaconazole, sold under the brand name Ertaczo among others, is an antifungal medication used to treat athlete's foot, ringworm, pityriasis versicolor, and candidiasis of the skin.[1] It is applied to the area of infection twice per day for 4 weeks.[1]
Common side effects include dry skin, burning skin, and inflamed skin.[1] Allergic reactions may occur.[1] It is in the azole class of medication.[1]
Sertaconazole was approved for medical use in the United States in 2003.[1] In the United States a 60 gram tube costs about 830 USD as of 2021.[2] This makes it significantly more expensive than generic and over the counter options.[3]
Medical uses
In randomized, double-blind, multicentre trials of 3 to 6 weeks' duration (n=127-383), a significantly greater number of patients with tinea of the glabrous skin and tinea pedis receiving a topical 2% sertaconazole cream once or twice daily achieved a successful mycological cure compared with recipients of a placebo cream.[4]
Side effects
Side effects were rarely reported with sertaconazole therapy, but may include contact dermatitis, burning on application site and skin dryness.
Pharmacology
Pharmacodynamics
Sertaconazole has several known mechanisms of action. It is considered fungistatic, fungicidal, antibacterial, antiinflammatory, antitrichomonal, and antipruritic.
Like other imidazole antifungals, sertaconazole blocks the synthesis of ergosterol by inhibiting the 14α-demethylase enzyme. Ergosterol is a critical component of the fungal cell membrane. Inhibition of ergosterol synthesis prevents fungal cells from multiplying and impairs hyphae growth.
Chemically, sertaconazole contains a benzothiophene ring which makes it unique from other imidazole antifungals. A benzothiophene ring is a sulfur analogue of the indole ring found in the amino acid tryptophan. Tryptophan is found in the fungal membrane in addition to lipids such as ergosterol. The benzothiophene ring in sertaconazole mimics tryptophan and increases the drugs ability to form pores in the fungal cell membrane. If the cell membrane is made sufficiently leaky by these pores the fungal cell will die from loss of ATP and other effects which can include calcium disregulation. These pores are believed to open at about 10 minutes following topical application of sertaconazole. One hour following topical application, approximately 90% of fungal cells die from lack of energy (due to ATP loss) and general loss of homeostasis. Sertaconazole is thought to be the only Benzothiophene antifungal with this mechanism of action.
Sertaconazole has also antiinflammatory and antipruritic action. It inhibits the release of proinflammatory cytokines from activated immune cells. It has been shown that sertaconazole activates the p38/COX2/PGE2 pathway. PGE2 can have a variety of important effects in the body including activation of the body's fever response.
Sertaconazole also has antibacterial action. It is hypothesized that the mechanism of action again involves sertaconazole's ability to form pores by mimicking tryptophan.
It has also been shown that sertaconazole can kill Trichomonas vaginalis in vitro. The exact mechanism of action is as yet unknown.
Sertaconazole also appears to inhibit the dimorphic transformation of Candida albicans into pathogenic fungi.
The following fungal organisms, among others, are known to be susceptible to sertaconazole:
- Candida albicans
- Epidermophyton floccosum
- Trichophyton mentagrophytes
- Trichophyton rubrum
Chemistry
Sertaconazole contains a stereocenter and consists of two enantiomers. The pharmaceutical drug is a racemate, an equal mixture of the (R)- and (S)-forms.[5]
| Enantiomers of sertaconazole | |
|---|---|
-Sertaconazol_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png.webp) (R)-Sertaconazole CAS number: 583057-48-1 |
-Sertaconazol_Structural_Formula_V1.svg.png.webp) (S)-Sertaconazole CAS number: 583057-51-6 |
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Sertaconazole Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 24 January 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ↑ "Ertaczo Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 7 November 2016. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ↑ Onion, Daniel K.; Glazer, James (25 October 2010). The Little Black Book of Primary Care. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 107. ISBN 978-1-4496-7197-6. Archived from the original on 12 October 2021. Retrieved 12 October 2021.
- ↑ Croxtall JD, Plosker GL (2009). "Sertaconazole: a review of its use in the management of superficial mycoses in dermatology and gynaecology". Drugs. 69 (3): 339–59. doi:10.2165/00003495-200969030-00009. PMID 19275277.
- ↑ Rote Liste 2017 – Arzneimittelverzeichnis für Deutschland (einschließlich EU-Zulassungen und bestimmter Medizinprodukte). Vol. 57. Frankfurt/Main: Rote Liste Service GmbH (Hrsg.). 2017. p. 217. ISBN 978-3-946057-10-9.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
- "Sertaconazole nitrate". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2021-03-27. Retrieved 2021-05-12.