Glanzmann's thrombasthenia
| Glanzmann's thrombasthenia | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Thrombasthenia of Glanzmann and Naegeli[1] | |
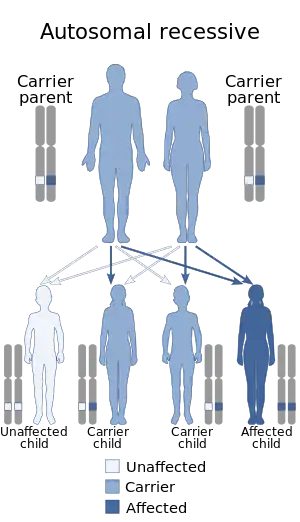 | |
| This condition is inherited in a autosomal recessive manner | |
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia is an abnormality of the platelets.[2] It is an extremely rare coagulopathy (bleeding disorder due to a blood abnormality), in which the platelets contain defective or low levels of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GpIIb/IIIa), which is a receptor for fibrinogen. As a result, no fibrinogen bridging of platelets to other platelets can occur, and the bleeding time is significantly prolonged.
Signs and symptoms
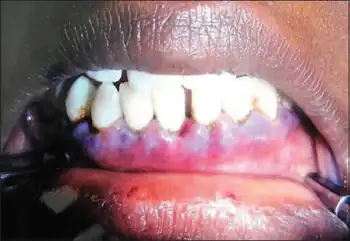
Characteristically, there is increased mucosal bleeding:[3]
- heavy menstrual bleeding
- easy bruising
- nosebleeds
- Bleeding from the gums
- gastrointestinal bleeding
- postpartum bleeding
- increased postoperative bleeding.
The bleeding tendency is variable but may be severe. Bleeding into the joints, particularly spontaneous bleeds, are very rare, in contrast to the hemophilias. Platelet numbers and morphology are normal. Platelet aggregation is normal with ristocetin, but impaired with other agonists such as ADP, thrombin, collagen, or epinephrine.
Cause
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia can be inherited in an autosomal recessive manner[3][4] or acquired as an autoimmune disorder.[3][5]
The bleeding tendency in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia is variable,[3] some individuals having minimal bruising, while others have frequent, severe, potentially fatal hemorrhages. Moreover, platelet αIIbβ3 levels correlate poorly with hemorrhagic severity, as virtually undetectable αIIbβ3 levels can correlate with negligible bleeding symptoms, and 10%–15% levels can correlate with severe bleeding.[6] Unidentified factors other than the platelet defect itself may have important roles.[3]
Pathophysiology
Glanzmann's thrombasthenia is associated with abnormal integrin αIIbβ3, formerly known as glycoprotein IIb/IIIa (GpIIb/IIIa),[7] which is an integrin aggregation receptor on platelets. This receptor is activated when the platelet is stimulated by ADP, epinephrine, collagen, or thrombin. GpIIb/IIIa is essential to blood coagulation since the activated receptor has the ability to bind fibrinogen (as well as von Willebrand factor, fibronectin, and vitronectin), which is required for fibrinogen-dependent platelet-platelet interaction (aggregation).In contrast, glycoproteinIb receptors are normal with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia. The role of GpIb is to enable platelet activation by contact with the von Willebrand factor-collagen complex that is exposed when the endothelial blood vessel lining is damaged. GpIb receptors are deficient in a disease known as Bernard–Soulier syndrome.
Understanding of the role of GpIIb/IIIa in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia led to the development of GpIIb/IIIa inhibitors, a class of powerful antiplatelet agents.[4][8]
Diagnosis
Light transmission aggregometry is widely accepted as the gold standard diagnostic tool for assessing platelet function, and a result of absent aggregation with any agonist except ristocetin is highly specific for Glanzmann's thrombasthenia.[9] Following is a table comparing its result with other platelet aggregation disorders:
| ADP | Epinephrine | Collagen | Ristocetin | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P2Y receptor inhibitor or defect[10] | Decreased | Normal | Normal | Normal |
| Adrenergic receptor defect[10] | Normal | Decreased | Normal | Normal |
| Collagen receptor defect[10] | Normal | Normal | Decreased or absent | Normal |
| Normal | Normal | Normal | Decreased or absent | |
| Decreased | Decreased | Decreased | Normal or decreased |
Treatment
Therapy involves both preventive measures and treatment of specific bleeding episodes.[3]
- Dental hygiene lessens gingival bleeding[11]
- Avoidance of antiplatelet agents such as aspirin and other anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen, and anticoagulants
- Iron or folate supplementation may be necessary if excessive or prolonged bleeding has caused anemia
- Hepatitis B vaccine
- Antifibrinolytic drugs such as tranexamic acid or ε-aminocaproic acid (Amicar)
- Desmopressin (DDAVP) does not normalize the bleeding time in Glanzmann's thrombasthenia but anecdotally improves hemostasis
- Hormonal contraceptives to control excessive menstrual bleeding
- Topical agents such as gelfoam, fibrin sealants, polyethylene glycol polymers, custom dental splints
- Platelet transfusions (only if bleeding is severe; risk of platelet alloimmunization)
- Recombinant factor VIIa, AryoSeven or NovoSeven FDA approved this drug for the treatment of the disease in July 2014.
- Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) for severe recurrent hemorrhages
Eponym
It is named after Eduard Glanzmann (1887-1959), the Swiss pediatrician who originally described it.[12][13][14]
History
The subsequent studies, following Eduard Glanzmann's description of hemorrhagic symptoms and “weak platelets” demonstrated that these patients have prolonged bleeding times and their platelets failed to aggregate in response to activation. In the mid-1970s, Nurden and Caen[15] and Phillips and colleagues[16] discovered that thrombasthenic platelets are deficient in integrins αIIbβ3.
See also
References
- ↑ "Glanzmann thrombasthenia | Genetic and Rare Diseases Information Center (GARD) – an NCATS Program". rarediseases.info.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 30 October 2019. Retrieved 30 October 2019.
- ↑ "Glanzmann thrombasthenia" at Dorland's Medical Dictionary
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Kaushansky K, Lichtman M, Beutler E, Kipps T, Prchal J, Seligsohn U. (2010; edition 8: pages 1933-1941) Williams Hematology. McGraw-Hill.ISBN 978-0071621519
- 1 2 Seligsohn, Uri (2002). "Glanzmann thrombasthenia: a model disease which paved the way to powerful therapeutic agents". Pathophysiology of Haemostasis and Thrombosis. 32 (5–6): 216–7. doi:10.1159/000073569. PMID 13679645.
- ↑ Tholouli E, Hay CR, O'Gorman P, Makris M (2004). "Acquired Glanzmann's thrombasthenia without thrombocytopenia: a severe acquired autoimmune bleeding disorder". Br. J. Haematol. 127 (2): 209–13. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.2004.05173.x. PMID 15461628.
- ↑ Nurden, Alan T (2006). "Glanzmann thrombasthenia". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 1: 10. doi:10.1186/1750-1172-1-10. PMC 1475837. PMID 16722529.
- ↑ Nurden, A. T.; Fiore, M.; Nurden, P.; Pillois, X. (2011). "Glanzmann thrombasthenia: a review of ITGA2B and ITGB3 defects with emphasis on variants, phenotypic variability, and mouse models". Blood. 118 (23): 5996–6005. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-07-365635. PMID 21917754.
- ↑ "Glanzmann Thrombasthenia Workup: Laboratory Studies, Histologic Findings". Archived from the original on 2018-03-11. Retrieved 2021-10-04.
- ↑ Solh, Melhem; Solh, Tia; Botsford, Ashley (2015). "Glanzmann's thrombasthenia: pathogenesis, diagnosis, and current and emerging treatment options". Journal of Blood Medicine: 219. doi:10.2147/JBM.S71319. ISSN 1179-2736.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Borhany, Munira; Pahore, Zaen; ul Qadr, Zeeshan; Rehan, Muhammad; Naz, Arshi; Khan, Asif; Ansari, Saqib; Farzana, Tasneem; Nadeem, Muhammad; Raza, Syed Amir; Shamsi, Tahir (2010). "Bleeding disorders in the tribe: result of consanguineous in breeding". Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases. 5 (1). doi:10.1186/1750-1172-5-23. ISSN 1750-1172.
- ↑ F.Z. Elmouatarif; B. Badre; S. Elarabi (2013). "Thrombasthénie de Glanzmann". Le Courrier du Dentiste. Archived from the original on 2017-08-09. Retrieved 2021-10-04.
- ↑ synd/1289 at Who Named It?
- ↑ Glanzmann, WE (1918). "Hereditäre hämorrhagische Thrombasthenie. Ein Beitrag zur Pathologie der Blutplättchen.[Hereditary haemorrhagic thrombasthenia. A contribution to the pathology of platelets] (German)". Jahrbuch für Kinderheilkunde [Yearbook of Pediatrics]. 88 (1–42): 113–141.
- ↑ Kannan, M.; Saxena, R. (2009). "Glanzmann's thrombasthenia: an overview". Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis. 15 (2): 152–165. doi:10.1177/1076029608326165. PMID 18930954. S2CID 25455222.
- ↑ Nurden AT,Caen JP (1974). "An abnormal platelet glycoprotein pattern in three cases of Glanzmann's thrombasthenia". British Journal of Haematology. 28 (2): 253–260. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2141.1974.tb06660.x. PMID 4473996.
- ↑ Phillips DR,Jenks CS,Luscher EF,Larrieu M (1975). "Molecular differences of exposed surface proteins on thrombasthenic platelet plasma membrane". Nature. 257 (5527): 599–600. Bibcode:1975Natur.257..599P. doi:10.1038/257599a0. PMID 1172605. S2CID 4188393.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
|