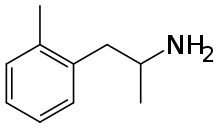
Ortetamine
Ortetamine (INN), also known as 2-methylamphetamine, is a stimulant drug of the amphetamine class. In animal drug discrimination tests it substituted for dextroamphetamine more closely than either 3- or 4-methylamphetamine, although with only around 1/10 the potency of dextroamphetamine itself.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ortetamine, O-Tolylaminopropane |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H15N |
| Molar mass | 149.237 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
| |
Legal status
Sweden's public health agency classified 2-MA as a narcotic substance, on January 18, 2019.[2] Ortetamine is an isomer of Methamphetamine, therefore, a Schedule II Controlled Substance in the United States.
See also
References
- Higgs RA, Glennon RA (December 1990). "Stimulus properties of ring-methyl amphetamine analogs". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 37 (4): 835–7. doi:10.1016/0091-3057(90)90571-x. PMID 2093186. S2CID 40060139.
- "Sexton nya ämnen klassas som narkotika eller hälsofarlig vara" (in Swedish). Folkhälsomyndigheten. 18 January 2019.
| Phenethylamines |
|
|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
|
| Phentermines |
|
| Cathinones |
|
| Phenylisobutylamines | |
| Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
|
| Miscellaneous |
|
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.