Cefapirin
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Intravenous, intramuscular |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| MedlinePlus | a601206 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H17N3O6S2 |
| Molar mass | 423.46 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Cefapirin (INN, also spelled cephapirin) is an injectable, antibiotic. It is marketed under the trade name Cefadyl. Production for use in humans has been discontinued in the United States.[1]
It is in the first-generation cephalosporin family of medications.[2]
It also has a role in veterinary medicine as Metricure, an intrauterine preparation, and combined with prednisolone in Mastiplan, an intramammary preparation. Both are licensed in cattle.
Synthesis
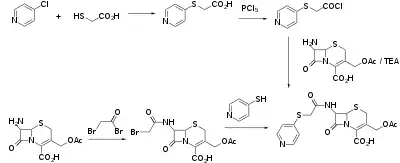
In one of the syntheses, 7-aminocephalosporanic acid (7-ACA) is reacted with bromoacetyl chloride to give the amide. The halo group is then displaced by 4-thiopyridine.[3]
References
- ↑ "CEFADYL". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Archived from the original on 2006-09-26. Retrieved 2020-09-20.
- ↑ Beauduy, Camille E.; Winston, Lisa G. (2020). "43. Beta-lactam and other cell wall - & membrane - active antibiotics". In Katzung, Bertram G.; Trevor, Anthony J. (eds.). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (15th ed.). New York: McGraw-Hill. p. 830. ISBN 978-1-260-45231-0. Archived from the original on 2021-10-10. Retrieved 2021-11-30.
- 1 2 Crast LB, Graham RG, Cheney LC (December 1973). "Synthesis of cephapirin and related cephalosporins from 7-(alpha-bromoacetamido)cephalosporanic acid". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 16 (12): 1413–5. doi:10.1021/jm00270a025. PMID 4148798.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.