Ibrexafungerp
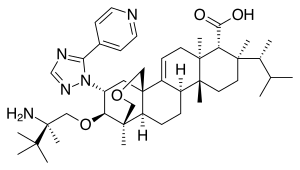 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | /aɪˌbrɛksəˈfʌndʒɜːrp/ eye-BREKS-ə-FUN-jurp |
| Trade names | Brexafemme |
| Other names | SCY-078 |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Antifungal |
| Main uses | Vaginal yeast infection[1] |
| Side effects | Diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, dizziness[1] |
| Interactions | CYP3A inhibitors[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth, intravenous |
| Typical dose | 300 mg BID x 1 day[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | >99%[1] |
| Metabolism | Hydroxylation (CYP3A4) then conjugation (glucuronidation, sulfation)[1] |
| Elimination half-life | 20 hours[1] |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C44H67N5O4 |
| Molar mass | 730.051 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Ibrexafungerp, sold under the brand name Brexafemme, is an antifungal medication used to treat vaginal yeast infection.[1] It may be used in females after the start of menstruation.[1] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, abdominal pain, and dizziness.[1] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[1] It is a triterpenoid antifungal and acts via blocking glucan synthase, which prevents formation of the fungal cell wall.[1]
Ibrexafungerp was approved for medical use in the United States in 2021.[1] It is not approved in Europe or the United Kingdom as of 2022.[2] In the United States a course of treatment costs about 500 USD as of 2022.[3]
Medical uses
Ibrexafungerp is indicated for the treatment of adult and postmenarchal pediatric females with vulvovaginal candidiasis (VVC).[1]
Dosage
It is taken at a dose of 300 mg twice for a single day.[1]
Pharmacology
An estimated 75% of women will have at least one episode of VVC and 40 to 45% will have two or more episodes in their lifetime.[4]
Pharmacodynamics
Ibrexafungerp is a triterpenoid antifungal agent.[1] It acts via inhibition of the enzyme glucan synthase, which is involved in the formation of 1,3-β-D-glucan—an essential component of the fungal cell wall.[1] The compound has concentration-dependent fungicidal activity against Candida species.[1]
Pharmacokinetics
Ibrexafungerp has a time to maximal concentrations of 4 to 6 hours.[1] It is metabolized by hydroxylation via CYP3A4 and subsequently by glucuronidation and sulfation.[1] The medication has an elimination half-life of approximately 20 hours.[1]
History
Ibrexafungerp is the first triterpenoid antifungal to be FDA approved.[1] It is the first, and so far only, non-azole oral antifungal to be FDA approved for the treatment of vaginal yeast infections.[5]
Research
Ibrexafungerp is undergoing trials for an intravenous formulation for the treatment of various fungal diseases, including fungal infections caused primarily by Candida (including C. auris) and Aspergillus species. It has demonstrated broad-spectrum antifungal activity against multidrug-resistant pathogens, including azole- and echinocandin-resistant strains.[6]
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 "Brexafemme- ibrexafungerp tablet, film coated". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 12 September 2021. Retrieved 12 September 2021.
- ↑ "Ibrexafungerp". SPS - Specialist Pharmacy Service. 2 August 2018. Archived from the original on 8 December 2021. Retrieved 29 October 2022.
- ↑ "Ibrexafungerp". Archived from the original on 29 October 2022. Retrieved 29 October 2022.
- ↑ "Vulvovaginal Candidiasis - STI Treatment Guidelines". www.cdc.gov. 2021-07-22. Archived from the original on 14 September 2022. Retrieved 2022-04-06.
- ↑ "Scynexis Announces FDA Approval of Brexafemme (ibrexafungerp tablets) as the First and Only Oral Non-Azole Treatment for Vaginal Yeast Infections". Scynexis, Inc. (Press release). 2 June 2021. Archived from the original on 31 December 2021. Retrieved 2 June 2021.
- ↑ "SCYNEXIS Announces Successful Completion of Phase 1 Trial Evaluating Intravenous (IV) Formulation of Ibrexafungerp". www.scynexis.com. Scynexis inc. 9 November 2021. Archived from the original on 20 October 2022. Retrieved 20 October 2022.
Further reading
- Azie N, Angulo D, Dehn B, Sobel JD (September 2020). "Oral Ibrexafungerp: an investigational agent for the treatment of vulvovaginal candidiasis". Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 29 (9): 893–900. doi:10.1080/13543784.2020.1791820. PMID 32746636.
- Davis MR, Donnelley MA, Thompson GR (July 2020). "Ibrexafungerp: A novel oral glucan synthase inhibitor". Med Mycol. 58 (5): 579–592. doi:10.1093/mmy/myz083. PMID 31342066.
- Petraitis V, Petraitiene R, Katragkou A, Maung BB, Naing E, Kavaliauskas P, et al. (May 2020). "Combination Therapy with Ibrexafungerp (Formerly SCY-078), a First-in-Class Triterpenoid Inhibitor of (1→3)-β-d-Glucan Synthesis, and Isavuconazole for Treatment of Experimental Invasive Pulmonary Aspergillosis". Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 64 (6). doi:10.1128/AAC.02429-19. PMC 7269506. PMID 32179521.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
- Clinical trial number NCT03734991 for "Efficacy and Safety of Oral Ibrexafungerp (SCY-078) vs. Placebo in Subjects With Acute Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (VANISH 303)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- Clinical trial number NCT03987620 for "Efficacy and Safety of Oral Ibrexafungerp (SCY-078) vs. Placebo in Subjects With Acute Vulvovaginal Candidiasis (Vanish 306)" at ClinicalTrials.gov