Trioxifene
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | LY-133,314 |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
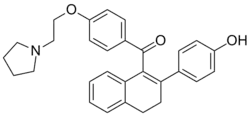
| Formula | C30H31NO3 |
| Molar mass | 453.582 g·mol−1 |
Trioxifene (INN) (developmental code name LY-133,314), or as the salt trioxifene mesylate (USAN), is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) with competitive binding activity against estradiol for the ERα and antagonistic activity against ERα-mediated gene expression, that was under preclinical and clinical development by Eli Lilly and Company for breast cancer and prostate cancer,[1] but was abandoned.[2]: 11 [3][4] Its affinity for the rat estrogen receptor was reported to be 20% relative to estradiol.[5][6]
References
- ↑ Neubauer BL, McNulty AM, Chedid M, Chen K, Goode RL, Johnson MA, Jones CD, Krishnan V, Lynch R, Osborne HE, Graff JR (September 2003). "The selective estrogen receptor modulator trioxifene (LY133314) inhibits metastasis and extends survival in the PAIII rat prostatic carcinoma model". Cancer Research. 63 (18): 6056–62. PMID 14522935.
- ↑ Philipp Y. Maximov, Russell E. McDaniel, V. Craig Jordan. Tamoxifen: Pioneering Medicine in Breast Cancer. Milestones in Drug Therapy. Springer Science & Business Media, 2013. ISBN 9783034806640
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 1252–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ I.K. Morton; Judith M. Hall (6 December 2012). Concise Dictionary of Pharmacological Agents: Properties and Synonyms. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 281–. ISBN 978-94-011-4439-1.
- ↑ Chander SK, Sahota SS, Evans TR, Luqmani YA (December 1993). "The biological evaluation of novel antioestrogens for the treatment of breast cancer". Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 15 (3): 243–69. doi:10.1016/1040-8428(93)90044-5. PMID 8142059.
- ↑ Robert J. Kavlock; George P. Daston (6 December 2012). Drug Toxicity in Embryonic Development II: Advances in Understanding Mechanisms of Birth Defects: Mechanistics Understanding of Human Development Toxicants. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 437–. ISBN 978-3-642-60447-8.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.