URB597
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
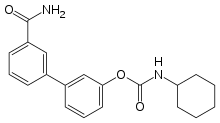
| Preferred IUPAC name
3′-Carbamoyl[1,1′-biphenyl]-3-yl cyclohexylcarbamate | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.164.994 |
| MeSH | URB597 |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C20H22N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 338.407 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
URB597 (KDS-4103) is a relatively selective and irreversible inhibitor of the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).[1][2] FAAH is the primary degradatory enzyme for the endocannabinoid anandamide and, as such, inhibition of FAAH leads to an accumulation of anandamide in the CNS and periphery where it activates cannabinoid receptors. URB597 has been found to elevate anandamide levels and have activity against neuropathic pain in a mouse model.[3]
URB597 was at one point being developed by Kadmus Pharmaceuticals, Inc. for clinical trials in humans.[4]
See also
References
- ↑ Mor, Marco; Rivara, S; Lodola, A; Plazzi, PV; Tarzia, G; Duranti, A; Tontini, A; Piersanti, G; Kathuria, S; Piomelli, Daniele (2004). "Cyclohexylcarbamic acid 3'- or 4'-substituted biphenyl-3-yl esters as fatty acid amide hydrolase inhibitors: synthesis, quantitative structure-activity relationships, and molecular modeling studies" (PDF). J Med Chem. 47 (21): 4998–5008. doi:10.1021/jm031140x. PMID 15456244.
- ↑ Alexander, JP; Cravatt, BF (2005). "Mechanism of Carbamate Inactivation of FAAH: Implications for the Design of Covalent Inhibitors and In Vivo Functional Probes for Enzymes". Chem. Biol. 12 (11): 1179–87. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2005.08.011. PMC 1994809. PMID 16298297.
- ↑ Russo, R; Loverme, J; La Rana, G; Compton, TR; Parrott, J; Duranti, A; Tontini, A; Mor, M; Tarzia, G; Calignano, A.; Piomelli, D. (2007). "The fatty-acid amide hydrolase inhibitor URB597 (cyclohexylcarbamicacid 3′-carbamoylbiphenyl-3-yl ester) reduces neuropathic pain after oral administration in mice" (PDF). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 322 (1): 236–42. doi:10.1124/jpet.107.119941. PMID 17412883. S2CID 40603248.
- ↑ Kadmus Pharmaceuticals official website Archived December 19, 2005, at the Wayback Machine
External links
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.