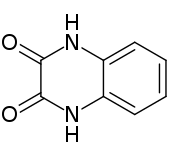
Quinoxalinedione
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,4-Dihydroquinoxaline-2,3-dione | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.036.259 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C8H6N2O2 |
| Molar mass | 162.15 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| Density | 1.549 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | > 300 °C (572 °F; 573 K) |
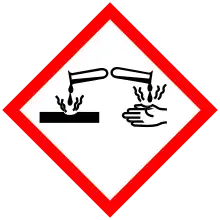
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
Pictograms |
  |
Signal word |
Warning |
Hazard statements |
H302, H315, H318, H319, H335 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa). | |
| Infobox references | |
Quinoxalinedione is an organic compound with the formula C6H4(NH)2(CO)2. It is a colorless solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. Quinoxalinediones are a family of related compounds sharing the same bicyclic core. Various quinoxalinediones are drugs.[1]
Synthesis and structure
Quinoxalinedione is produced by condensation of dimethyloxalate and o-phenylenediamine:
- C2O2(OMe)2 + C6H4(NH2)2 → C6H4(NH)2(CO)2 + 2 MeOH
The compound exists in solution and the solid state predominantly as the diamide form.[2] Some reactions of the compound indicate a role for the diol tautomer.
Drugs based on quinoxalinediones
Quinoxalinediones act as antagonists of the AMPA, kainate, and/or NMDA receptors of the ionotropic glutamate receptor family.[3][4][5][6] Examples include the following:
- ACEA-1011
- Becampanel
- CNQX
- DNQX
- Fanapanel (MPQX)
- Licostinel (ACEA-1021)
- NBQX
- PNQX
- YM90K
- Zonampanel
A drug closely related to the quinoxalinediones, but possessing a quinazoline-2,4-dione structure instead, is selurampanel. Caroverine is another closely related drug to the above, but instead containing a quinoxaline-2-one structure.
References
- ↑ Poulie, Christian B. M.; Bunch, Lennart (2013). "Heterocycles as Nonclassical Bioisosteres of α-Amino Acids". ChemMedChem. 8 (2): 205–215. doi:10.1002/cmdc.201200436. PMID 23322633. S2CID 38623973.
- ↑ Saied M. Soliman, Jörg Albering, Morsy A.M. Abu-Youssef "Low temperature X-ray molecular structure, tautomerism and spectral properties of 2,3-dihydroxyquinoxaline" Journal of Molecular Structure 2013, vol. 1053, pp. 48–60. doi:10.1016/j.molstruc.2013.09.005
- ↑ Ashley, M.J. (2010). Traumatic Brain Injury: Rehabilitation, Treatment, and Case Management, Third Edition. CRC Press. p. 142. ISBN 978-1-4398-4982-8. Retrieved 2015-01-01.
- ↑ Turski, L.; Schoepp, D.D.; Cavalheiro, E.A. (2001). Excitatory Amino Acids: Ten Years Later. Biomedical and health research (in Italian). IOS Press. p. 38. ISBN 978-1-58603-072-8. Retrieved 2015-01-01.
- ↑ Offermanns, S.; Rosenthal, W. (2008). Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. Encyclopedia of Molecular Pharmacology. Springer. p. 660. ISBN 978-3-540-38916-3. Retrieved 2015-01-01.
- ↑ Dudić, Adela; Reiner, Andreas (2019). "Quinoxalinedione deprotonation is important for glutamate receptor binding". Biological Chemistry. 400 (7): 927–938. doi:10.1515/hsz-2018-0464. PMID 30903748.