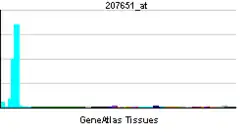
GPR171
Probable G-protein coupled receptor 171 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GPR171 gene.[5][6]
| GPR171 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Aliases | GPR171, H963, G protein-coupled receptor 171 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| External IDs | MGI: 2442043 HomoloGene: 36330 GeneCards: GPR171 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wikidata | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
- GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000174946 - Ensembl, May 2017
- GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000050075 - Ensembl, May 2017
- "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- Jacobs KA, Collins-Racie LA, Colbert M, Duckett M, Golden-Fleet M, Kelleher K, Kriz R, LaVallie ER, Merberg D, Spaulding V, Stover J, Williamson MJ, McCoy JM (Dec 1997). "A genetic selection for isolating cDNAs encoding secreted proteins". Gene. 198 (1–2): 289–96. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00330-2. PMID 9370294.
- "Entrez Gene: GPR171 G protein-coupled receptor 171".
Further reading
- Adams MD, Kerlavage AR, Fleischmann RD, et al. (1995). "Initial assessment of human gene diversity and expression patterns based upon 83 million nucleotides of cDNA sequence" (PDF). Nature. 377 (6547 Suppl): 3–174. PMID 7566098.
- Joensuu T, Hämäläinen R, Yuan B, et al. (2001). "Mutations in a novel gene with transmembrane domains underlie Usher syndrome type 3". Am. J. Hum. Genet. 69 (4): 673–84. doi:10.1086/323610. PMC 1226054. PMID 11524702.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. Bibcode:2002PNAS...9916899M. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.