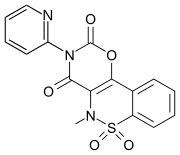
Droxicam
Droxicam is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug of the oxicam class. A prodrug of piroxicam, it is used for the relief of pain and inflammation in musculoskeletal disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C16H11N3O5S |
| Molar mass | 357.34 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
References
- Jané F, Rodríguez de la Serna A (1991). "Droxicam: a pharmacological and clinical review of a new NSAID". European Journal of Rheumatology and Inflammation. 11 (4): 3–9. PMID 1365488.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.