Proglumetacin
Proglumetacin (usually as the maleate salt, trade names Afloxan, Protaxon and Proxil) is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). It is metabolized in the body to indometacin and proglumide,[1] a drug with antisecretory effects that helps prevent injury to the stomach lining.
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
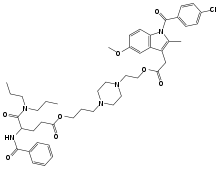
| Other names | 3-[4-[2-[2-[1-(4-chlorobenzoyl)-5-methoxy-2-methylindol-3-yl]acetyl]oxyethyl]piperazin-1-yl]propyl 4-(benzoylamino)-5-(dipropylamino)-5-oxopentanoate |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | Hepatic. Undergoes enterohepatic recirculation |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C46H58ClN5O8 |
| Molar mass | 844.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
References
- Setnikar I, Arigoni R, Chisté R, Makovec F, Revel L (1987). "Plasma levels of proglumetacin and its metabolites after intravenous or oral administration in the dog". Arzneimittel-Forschung. 37 (6): 698–702. PMID 3663267.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.