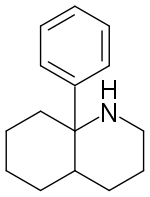
8A-PDHQ
8a-Phenyldecahydroquinoline (8A-PDHQ) is a high affinity NMDA antagonist developed by a team at Parke Davis in the 1950s.[1] It is a structural analog of phencyclidine with slightly lower binding affinity than the parent compound. (-)-8a-Phenyldecahydroquinoline has an in vivo potency comparable to that of (+)-MK-801.[2][3]
 | |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H21N |
| Molar mass | 215.340 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
References
- US Patent 3035059
- Chen C, Kozikowski AP, Wood PL, Reynolds IJ, Ball RG, Pang YP (May 1992). "Synthesis and biological activity of 8a-phenyldecahydroquinolines as probes of PCP's binding conformation. A new PCP-like compound with increased in vivo potency". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 35 (9): 1634–8. doi:10.1021/jm00087a020. PMID 1315871.
- Elhallaoui M, Laguerre M, Carpy A, Ouazzani FC (February 2002). "Molecular modeling of noncompetitive antagonists of the NMDA receptor: proposal of a pharmacophore and a description of the interaction mode". Journal of Molecular Modeling. 8 (2): 65–72. doi:10.1007/s00894-001-0067-4. PMID 12032600.
| AMPARTooltip α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor |
|
|---|---|
| KARTooltip Kainate receptor |
|
| NMDARTooltip N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
|
| |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.