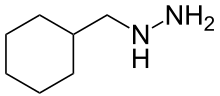
Cimemoxin
Cimemoxin (INN), or cyclohexylmethylhydrazine, is a hydrazine monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant which was never marketed.[1]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C7H16N2 |
| Molar mass | 128.219 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Synthesis
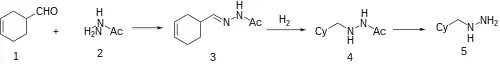
It possesses 50 times the relative activity of iproniazid and 25x nialamide (see patent).
3-Cyclohexene-1-carbaldehyde [100-50-5] (aka 1,2,3,6-Tetrahydrobenzaldehyde) is reacted with N-acetylhydrazine to give the hydrazone, which is reduced by catalytic hydrogenation. The acetyl group is removed by acid hydrolysis.
References
- World Health Organization (2011). "The use of stems in the selection of International Nonproprietary Names (INN) for pharmaceutical substances" (PDF). Retrieved 2012-05-20.
- Boissier JR, Ratouis R, Dumont C, Lesbros J (1966). "Synthesis of new monoamine oxidase inhibitors". Chimica Therapeutica (5–6): 320–326.
- FR 1405420, Boissier JR, Ratouis R, "ouvelle hydrazine et ses sels et procédé de préparation", issued 1965, assigned to Soc Ind Fab Antibiotiques Sifa.
- GB 1102228, "N-hexahydrobenzyl hydrazine and its salts and process for preparation thereof", issued 1968, assigned to Soc Ind Fab Antibiotiques Sifa.
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.