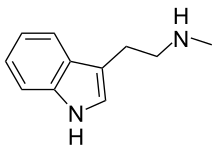
N-Methyltryptamine
N-Methyltryptamine (NMT) is a member of the substituted tryptamine chemical class and a natural product which is biosynthesized in the human body from tryptamine by certain N-methyltransferase enzymes, such as indolethylamine N-methyltransferase.[1][2] It is a common component in human urine.[3] NMT is an alkaloid derived from L-tryptophan that has been found in the bark, shoots and leaves of several plant genera, including Virola, Acacia, Mimosa, and Desmanthus—often together with the related compounds N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT) and 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine (5-MeO-DMT).
 | |
| Legal status | |
|---|---|
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.000.462 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H14N2 |
| Molar mass | 174.247 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 87 to 89 °C (189 to 192 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
Orally administered NMT appears to produce no psychoactive effects, likely as a result of extensive first-pass metabolism.[4] However, it may become active upon combination with a MAOA inhibitor (MAOI).[4] By vaporization NMT shows activity at 50–100 mg, with a duration of 45–70 minutes; duration of visual effects 15–30 seconds. Effects are primarily non-visual.[5][6]
Legality
In the United States N-Methyltryptamine is considered a schedule 1 controlled substance as an positional isomer of Alpha-methyltryptamine (AMT) [7]
See also
- N-Ethyltryptamine (NET)
- N,N,-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT)
- Acacia confusa (a natural source of NMT, with other tryptamines, 1.63%. Buchanan et al. 2007)
- Acacia obtusifolia (NMT up to 2/3 alkaloid content)
- Acacia simplicifolia (synon. A. simplex) (1.44% NMT in bark, 0.29% twigs, Pouet et al. 1976)
- Desmanthus illinoensis (NMT major component seasonally)
References
- Lindemann L, Hoener MC (May 2005). "A renaissance in trace amines inspired by a novel GPCR family". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 26 (5): 274–281. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2005.03.007. PMID 15860375.
- Burchett SA, Hicks TP (August 2006). "The mysterious trace amines: protean neuromodulators of synaptic transmission in mammalian brain". Progress in Neurobiology. 79 (5–6): 223–246. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.07.003. PMID 16962229. S2CID 10272684.
- Forsström T, Tuominen J, Karkkäinen J (2001). "Determination of potentially hallucinogenic N-dimethylated indoleamines in human urine by HPLC/ESI-MS-MS". Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation. 61 (7): 547–56. doi:10.1080/003655101753218319. PMID 11763413. S2CID 218987277.
- Foye WO, Lemke TL, Williams DA (2002). "Hallucinogens, Stimulatants, and Drugs of Abuse". Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry (5th ed.). p. 439. ISBN 9780683307375.
- Shulgin A, Shulgin A (1997). TIKHAL. Berkeley: Transform Press.
- Nen - lecture presented EGA conference, Victoria, Australia 4/12/2011; and Breaking Conventions, London 12/7/2013.
- "Orange Book - List of Controlled Substances and Regulated Chemicals" (PDF). U.S. Department of Justice Diversion Control Division. August 2023. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 6, 2023.
External links
| Amino acid-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lipid-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Nucleobase-derived |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Vitamin-derived | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Miscellaneous |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT1 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT2 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5-HT3–7 |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|