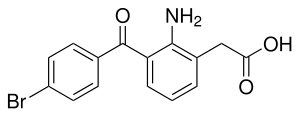
Bromfenac
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Bromday, Xibrom, Prolensa, Yellox, others |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | NSAID[1] |
| Main uses | Pain after cataract surgery[1] |
| Side effects | Red eyes, itchy eyes, headache[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Eye drops |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a611018 |
| Legal | |
| License data | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Protein binding | 99.8% |
| Metabolism | CYP2C9 |
| Metabolites | Lactam, others |
| Elimination half-life | 1.4 hours in aqueous humour |
| Excretion | 82% urine, 13% faeces |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H12BrNO3 |
| Molar mass | 334.169 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 284 to 286 °C (543 to 547 °F) (bromfenac sodium·1.5H2O) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Bromfenac is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) which is used for pain and inflammation after cataract surgery.[1] It is used as an eye drop twice per day for two weeks.[1]
Common side effects include red eyes, itchy eyes, and headache.[1] Other side effects may include slower wound healing, bleeding, and keratitis.[1] It works by blocking the production of prostaglandins.[1]
Bromfenac was approved for medical use in the United States in 2005.[1] It is available as a generic medication.[2] In the United States 1.7 ml of 0.09% solution costs about 51 USD as of 2021.[2] In the United Kingdom 5 ml of the solution costs the NHS 8.5 pounds.[3]
Medical uses
Bromfenac is used for the treatment of postoperative ocular inflammation following cataract extraction.[4][5]
It reduces macular edema and thickness of the retina (an indicator for inflammation) and improve visual acuity after surgery.[6]
Contraindications
Bromfenac is contraindicated for people with adverse reactions to NSAIDs, such as asthma or rashes.[7][8]
Side effects
Bromfenac eye drops are generally well tolerated. Comparatively common side effects in clinical studies included abnormal sensations in eye (0.5% of people treated with bromfenac), mild to moderate erosion of the cornea (0.4%), eye pruritus (0.4%), eye pain (0.3%) and redness (0.3%). Serious side effects such as corneal perforation were not reported in studies but only during post-marketing in less than one patient in 1000.[7][8]
Interactions
No systematic interaction studies have been performed. There are no known cases of interactions with antibiotic eye drops.[7][8] Blood plasma levels remain very low during bromfenac therapy, so interactions with drugs taken by mouth are unlikely.
Pharmacology
Mechanism of action
As an NSAID, bromfenac works by inhibiting prostaglandin synthesis by blocking the cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes. It preferably acts on COX-2 and only has a low affinity for COX-1.[8]
Pharmacokinetics
Bromfenac is well absorbed through the cornea and reaches highest concentrations in the aqueous humour after 150 to 180 minutes, with a biological half-life of 1.4 hours and high drug levels being maintained for at least 12 hours. It is mainly concentrated in the aqueous humour and conjunctiva, and much less in the lens and vitreous body.[7][8]
Concentrations in the blood plasma are too low to be measured quantitatively. 99.8% of the substance are bound to plasma proteins. The enzyme mainly responsible for metabolization of bromfenac is CYP2C9, and metabolites include the lactam and several conjugated compounds. 82% are excreted via the urine, and 13% via the faeces.[7][8]
The high degree of penetration and potency of bromfenac can be attributed to the halogenation of the molecule: by adding a bromine the NSAID becomes highly lipophilic which allows for rapid, sustained drug levels in the ocular tissues.
Chemistry
Along with indomethacin, diclofenac and others, bromfenac belongs to the acetic acid group of NSAIDs. It is used in form of bromfenac sodium · 1.5 H2O (CAS number: 120638-55-3 ), which is soluble in water, methanol and aqueous bases, insoluble in chloroform and aqueous acids, and melts at 284 to 286 °C (543 to 547 °F) under decomposition.[9]
History

For ophthalmic use, bromfenac has been prescribed more than 20,000,000 times across the world.[8] As an eye drop, it has been available since 2000, starting in Japan where it was sold as Bronuck.[10] It was first FDA approved for use in the United States in 2005, and it was marketed as Xibrom, twice-daily.[11] In October 2010 Bromday received FDA approval as a new, once-daily formulation. More recently, in 2013, Prolensa has also been approved by the FDA.[11] Bromfenac eye drops have been marketed in the European Union since 2011,[8] and are available on worldwide markets with agreements from Bausch & Lomb,[8] Croma-Pharma, and other companies.
Bromfenac was formerly marketed in the United States by Wyeth-Ayerst in an oral formulation called Duract for short-term relief of pain (less than 10 days at a time). It was brought to market in July 1997, and was withdrawn 22 June 1998, following numerous reports of hepatotoxicity in patients who had taken the medication for longer than the recommended 10-day period.[12][13]
Society and culture
Cost
Bromfenac ophthalmic ophthalmic solution in the U.S. of 1.7 milliliters, goes for about $130 (USD)[14]
.svg.png.webp) Bromfenac costs (US)
Bromfenac costs (US).svg.png.webp) Bromfenac prescriptions (US)
Bromfenac prescriptions (US)
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Bromfenac Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 21 January 2021. Retrieved 17 July 2021.
- 1 2 "Bromfenac Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Archived from the original on 26 May 2020. Retrieved 17 July 2021.
- ↑ BNF (80 ed.). BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 1241. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ↑ "Yellox EPAR". European Medicines Agency (EMA). Archived from the original on 10 January 2021. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ↑ "Prolensa- bromfenac sodium solution/ drops". DailyMed. 1 March 2020. Archived from the original on 28 February 2021. Retrieved 23 November 2020.
- ↑ Sheppard JD (2016). "Topical bromfenac for prevention and treatment of cystoid macular edema following cataract surgery: a review". Clinical Ophthalmology. 10: 2099–2111. doi:10.2147/OPTH.S86971. PMC 5087782. PMID 27822006.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Haberfeld H, ed. (2015). Austria-Codex (in German). Vienna: Österreichischer Apothekerverlag.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 "Yellox Summary of Product Characteristics" (PDF). European Medicines Agency. 11 January 2016. Archived (PDF) from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ Dinnendahl V, Fricke U, eds. (2012). Arzneistoff-Profile (in German). Vol. 2 (26 ed.). Eschborn, Germany: Govi Pharmazeutischer Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7741-9846-3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: unrecognized language (link) - ↑ "Ethical Products for Medical Professionals". Senju Pharmaceutical. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- 1 2 FDA Professional Drug Information for Xibrom.
- ↑ Hunter EB, Johnston PE, Tanner G, Pinson CW, Awad JA (August 1999). "Bromfenac (Duract)-associated hepatic failure requiring liver transplantation". The American Journal of Gastroenterology. 94 (8): 2299–301. PMID 10445569.
- ↑ "Duract (bromfenac) Information". FDA. Archived from the original on 27 September 2019. Retrieved 11 December 2016.
- ↑ "Bromfenac ophthalmic Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 20 January 2021. Retrieved 25 March 2021.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|
- "Bromfenac". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2021-04-17. Retrieved 2020-11-24.
- "Bromfenac sodium". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2021-04-13. Retrieved 2020-11-24.