Loxoprofen
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral, transdermal |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Protein binding | 97% |
| Metabolism | Liver glucuronidation |
| Elimination half-life | 75 minutes |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
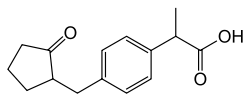
| Formula | C15H18O3 |
| Molar mass | 246.306 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Chirality | Racemic mixture |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Loxoprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) in the propionic acid derivatives group, which also includes ibuprofen and naproxen among others. It is available in some countries for oral administration. A transdermal preparation was approved for sale in Japan on January 2006;[1] medicated tape and gel formulations followed in 2008 and 2010.
It was patented in 1977 and approved for medical use in 1986.[2]
Pharmacokinetics
Loxoprofen is a prodrug. It is quickly converted to its active trans-alcohol metabolite following oral administration, and reaches its peak plasma concentration within 30 to 50 minutes.
Mechanism of action
As most NSAIDs, loxoprofen is a non-selective cyclooxygenase inhibitor, and works by reducing the synthesis of prostaglandins from arachidonic acid.
Interactions
Loxoprofen should not be administered at the same time as second-generation quinolone antibiotics such as ciprofloxacin and norfloxacin, as it increases their inhibition of GABA and this may cause seizures.[3] It may also increase the plasma concentration of warfarin, methotrexate, sulfonylurea derivatives and lithium salts, so care should be taken when loxoprofen is administered to patients taking any of these drugs.[3]
Brand names
It is marketed in Brazil, Mexico and Japan by Sankyo as its sodium salt, loxoprofen sodium, under the trade name Loxonin; in Argentina as Oxeno; in India as Loxomac; in Thailand as Japrolox; and in Saudi Arabia as Roxonin.
A biosimilar is marketed in Brazil by Aché as Oxotron. In Japan, two fixed dose combinations are available: Loxonin S Plus, with magnesium oxide, and Loxonin S Premium, with apronal, caffeine, and aluminium magnesium silicate.
References
- ↑ Daiichi Sankyo Co. (January 24, 2006). "Percutaneous Absorption-Type Analgesic and Anti-inflammatory Drug Loxonin Poultice 100mg Receives Approval for Manufacture" (Press release). Doctor's Guide Global Edition. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
- ↑ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 521. ISBN 9783527607495.
- 1 2 "LOXONIN - Bula do Medicamento [Label Information]" (in Portuguese). Centralx. 2007. Retrieved 2007-04-19.
| Wikimedia Commons has media related to Loxoprofen. |