Ramatroban
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Baynas |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral (tablets) |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.159.668 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
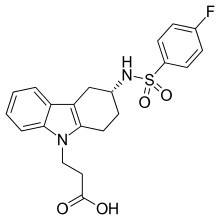
| Formula | C21H21FN2O4S |
| Molar mass | 416.47 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Ramatroban (INN) (also known as Bay-u3405)[1] is a thromboxane receptor antagonist.[2]
It is also a DP2 receptor antagonist.[3]
It is indicated for the treatment of coronary artery disease.[4] It has also been used for the treatment of asthma.[5]
It has been suggested that Ramatroban, by modulating DP2 receptor, can reverse viremia-associated proinflammatory and prothrombotic processes which are similar to those induced by SARS-Cov-2. Hence, Ramatroban, that has been used for the treatment of allergic rhinitis in Japan for the past two decades with a well established safety profile, merits investigation as a novel immunotherapy for the treatment of COVID-19 disease, although no clinical trial has yet been conducted.[6]
Ramatroban was developed by the German pharmaceutical company Bayer AG and is co-marketed in Japan by Bayer and Nippon Shinyaku Co. Ltd. under the trade name Baynas.
References
- ↑ "Ramatroban (compound)". PubChem. National Center for Biotechnology Information. Retrieved 22 June 2019.
- ↑ Sugimoto H, Shichijo M, Iino T, et al. (April 2003). "An orally bioavailable small molecule antagonist of CRTH2, ramatroban (BAY u3405), inhibits prostaglandin D2-induced eosinophil migration in vitro". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 305 (1): 347–52. doi:10.1124/jpet.102.046748. PMID 12649388. S2CID 10016709.
- ↑ Royer JF, Schratl P, Carrillo JJ, et al. (September 2008). "A novel antagonist of prostaglandin D2 blocks the locomotion of eosinophils and basophils". Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 38 (9): 663–71. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2362.2008.01989.x. PMID 18837743.
- ↑ Fiedler VB, Seuter F, Perzborn E (December 1990). "Effects of the novel thromboxane antagonist Bay U 3405 on experimental coronary artery disease" (PDF). Stroke. 21 (12 Suppl): IV149–51. PMID 2260140.
- ↑ Endo S, Akiyama K (November 1996). "[Thromboxane A2 receptor antagonist in asthma therapy]". Nippon Rinsho (in Japanese). 54 (11): 3045–8. PMID 8950952.
- ↑ Rizk JG, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Mehra MR, Lavie CJ, Rizk Y, Forthal DN (September 2020). "Pharmaco-Immunomodulatory Therapy in COVID-19". Drugs. 80 (13): 1267–1292. doi:10.1007/s40265-020-01367-z. PMC 7372203. PMID 32696108.
External links
- (in Japanese) Baynas Tablets Prescribing Information