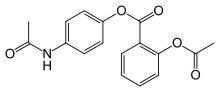
Benorilate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.023.340 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C17H15NO5 |
| Molar mass | 313.309 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| | |
Benorilate (INN), or benorylate, is an ester-linked codrug of aspirin with paracetamol. It is used as an anti-inflammatory and antipyretic medication. In the treatment of childhood fever, it has been shown to be inferior to paracetamol and aspirin taken separately. In addition, because it is converted to aspirin, benorylate is not recommended in children due to concerns about Reye syndrome.[1]
References
- ↑ Similä S, Keinänen S, Kouvalainen K (December 1975). "Oral antipyretic therapy: evaluation of benorylate, an ester of acetylsalicylic acid and paracetamol". European Journal of Pediatrics. 121 (1): 15–20. doi:10.1007/bf00464391. PMID 2478. S2CID 21112438.
| pyrazolones / pyrazolidines | |
|---|---|
| salicylates | |
| acetic acid derivatives and related substances | |
| oxicams |
|
| propionic acid derivatives (profens) |
|
| n-arylanthranilic acids (fenamates) | |
| COX-2 inhibitors (coxibs) | |
| other |
|
| NSAID combinations | |
Key: underline indicates initially developed first-in-class compound of specific group; #WHO-Essential Medicines; †withdrawn drugs; ‡veterinary use. | |
| |
|
Prostanoid signaling modulators | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Receptor (ligands) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Enzyme (inhibitors) |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.