Remifentanil
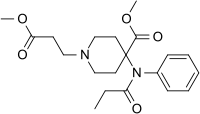 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Ultiva, others |
| Other names | methyl 1-(2-methoxycarbonylethyl)-4-(phenyl-propanoyl-amino)-piperidine-4-carboxylate |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Opioid[1] |
| Main uses | Anesthesia[1] |
| Side effects | Respiratory depression (decreased breathing), slow heart rate, low blood pressure, stiff muscles, nausea, itchiness[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Intravenous |
| Onset of action | Within 90 sec[1] |
| Duration of action | Up to 15 minutes[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| Legal | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | Not applicable (intravenous administration) |
| Protein binding | 70% (bound to plasma proteins) |
| Metabolism | cleaved by non-specific plasma and tissue esterases |
| Elimination half-life | 1-20 minutes |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H28N2O5 |
| Molar mass | 376.453 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 5 °C (41 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Remifentanil, sold under the brand name Ultiva among others, is an opioid medication used to treat during anesthesia to manage pain.[1] It is given by injection into a vein.[1] Effects begin within 90 seconds and last up to 15 minutes.[1]
Common side effects include respiratory depression (decreased breathing), slow heart rate, low blood pressure, stiff muscles, nausea, and itchiness.[1] Breastfeeding is not recommended for 24 hours after use.[2] It works by activating the mu opioid receptor.[1]
Remifentanil was approved for medical use in the United States in 1996.[1] It is available as a generic medication.[2] In the United Kingdom 1 mg costs the NHS about £5 as of 2021.[1] In the United States this amount costs about 55 USD.[3] In the United States it is classified as a Schedule II controlled substance.[1]
Medical use
Remifentanil is used as an opioid analgesic that has a rapid onset and rapid recovery time.[4] It has been used effectively during craniotomies,[5] spinal surgery,[6] cardiac surgery,[7] and gastric bypass surgery.[8] While opiates function similarly, with respect to analgesia, the pharmacokinetics of remifentanil[9] allows for quicker post-operative recovery.[10]
Dosage
In adults it is given as an intravenous infusion in doses ranging from 0.1 µg/kg/min to 0.5 µg/kg/min. Children may require higher infusion rates (up to 1.0 (µg/kg)/min).[11] The clinically useful infusion rates are 0.025-0.1 (µg/kg)/min for sedation (rates adjusted to age of patient, severity of their illness and invasiveness of surgical procedure). Small amounts of other sedative medications are usually co-administered with remifentanil to produce sedation. Clinically useful infusion rates in general anesthesia vary but are usually 0.1-1 µg/kg/min.[12]
Remifentanil can be administered as part of an anesthesia technique called TIVA (Total Intravenous Anesthesia) using computer controlled infusion pumps in a process called target controlled infusion (TCI). A target plasma concentration is entered as ng/ml into the pump, which calculates its infusion rate according to patient factors like age and weight. Induction levels of 40 ng/ml are commonly used, but it generally varies between 3-8 ng/ml. For certain surgical procedures that produce particularly strong stimuli a level of up to 15 ng/ml might be needed. The relatively short context-sensitive half-life of Remifentanil allows the desired blood plasma level to be achieved quickly and also for the same reason, recovery occurs quickly. This allows remifentanil to be used in unique circumstances such as cesarean section.[13]
Remifentanil's short context-sensitive half-life makes it ideal for intense pain of short duration. As such, it has been used for analgesia in labor successfully; however, it is not as effective as epidural analgesia.[14]
In combination with propofol, remifentanil is used for anesthesia of patients undergoing electroconvulsive therapy.[15]
Side effects
Remifentanil is a specific μ-receptor agonist.[16] Hence, it causes a reduction in sympathetic nervous system tone, respiratory depression and analgesia. The drug's effects include a dose-dependent decrease in heart rate and arterial pressure and respiratory rate and tidal volume. Muscle rigidity is sometimes noted.
The most common side effects reported by patients receiving this medication are a sense of extreme "dizziness" (often short lived, a common side effect of other fast-acting synthetic phenylpiperidine narcotics such as fentanyl and alfentanil) and intense itching (pruritus), often around the face. These side effects are often controlled by either altering the administered dose (decreasing or in some cases, increasing the dose) or by administering other sedatives that allow the patient to tolerate or lose awareness of the side effect.
Because pruritus is due to excessive serum histamine levels, antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl) are often co-administered. This is done with care, however, as excessive sedation may occur.
Nausea can occur as a side effect of remifentanil, however, it is usually transient in nature due to the drug's short half-life which rapidly removes it from the patient's circulation once the infusion is terminated.
Abuse
Remifentanil, being a μ-receptor agonist, functions like other μ-receptor agonists, such as morphine and codeine, and can cause euphoria and has the potential for abuse.[17][18] However, due to its rapid metabolism and short-acting half-life the likelihood of becoming abused is quite low. Nevertheless, there have been some documentations of remifentanil abuse.[19][20]
Pharmacology
Metabolism
Remifentanil is considered a metabolic soft drug,[21] one that is rapidly metabolized to an inactive form. Unlike other synthetic opioids which are hepatically metabolized, remifentanil has an ester linkage which undergoes rapid hydrolysis by non-specific tissue and plasma esterases. This means that accumulation does not occur with remifentanil and its context-sensitive half-life remains at 4 minutes after a 4-hour infusion.
Remifentanil is metabolized to a compound (remifentanil acid) which has 1/4600th the potency of the parent compound.[22]
Due to its quick metabolism and short effects, remifentanil has opened up new possibilities in anesthesia. When remifentanil is used together with a hypnotic (i.e. one that produces sleep) it can be used in relative high doses. This is because remifentanil will be rapidly eliminated from the blood plasma on termination of the remifentanil infusion, hence the effects of the drug will quickly dissipate even after very long infusions. Owing to synergism between remifentanil and hypnotic drugs (such as propofol) the dose of the hypnotic can be substantially reduced.[16] This leads often to more hemodynamic stability during surgery and a quicker post-operative recovery time.
Potency
Comparing its analgesic effect, remifentanil is superior to morphine[23] but not to fentanyl.[24]
History
Prior to the development of remifentanil, most short-acting hypnotics and amnestics faced issues with prolonged use, where accumulation would result in unfavorable lingering effects during post-operative recovery. Remifentanil was designed to serve as a strong anesthetic with an ultra-short and predictable duration that would not have accumulation issues.[25]
Remifentanil is patented by Glaxo Wellcome Inc.[26] and was FDA approved on July 12, 1996.[27] It's patent ended at the 10th of September 2017.
Society and culture
Cost
- 1 mg vial - US$30.19
- 3 mg vial - US$57.20
- 5 mg vial - US$118.15
Regulation
In Hong Kong, remifentanil is regulated under Schedule 1 of Hong Kong's Chapter 134 Dangerous Drugs Ordinance. It can only be used legally by health professionals and for university research purposes. The substance can be given by pharmacists under a prescription. Anyone who supplies the substance without prescription can be fined $10000 (HKD). The penalty for trafficking or manufacturing the substance is a $5,000,000 (HKD) fine and life imprisonment. Possession of the substance for consumption without license from the Department of Health is illegal with a $1,000,000 (HKD) fine and/or 7 years of jail time.
Remifentanil is a Schedule II narcotic controlled substance in the United States with a DEA ACSCN of 9739 and a 2013 annual aggregate manufacturing quota of 3750 grams, unchanged from the prior year.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 "Remifentanil Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 5 March 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- 1 2 BNF (80 ed.). BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. September 2020 – March 2021. p. 1415. ISBN 978-0-85711-369-6.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: date format (link) - ↑ "Remifentanil Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 20 April 2021. Retrieved 16 October 2021.
- ↑ "Remifentanil, IV opioid analgesic, Remi | Ultiva". www.ultiva.com. Archived from the original on 2019-04-20. Retrieved 2015-11-30.
- ↑ Gesztesi Z, Mootz BL, White PF. The use of a remifentanil infusion for hemodynamic control during intracranial surgery. Anesth Analg. 1999;89(5):1282-1287
- ↑ Grottke O, Dietrich PJ, Wiegels S, Wappler F. Intraoperative wake-up test and postoperative emergence in patients undergoing spinal surgery: a comparison of intravenous and inhaled anesthetic techniques using short-acting anesthetics. Anesth Analg. 2004;99(5):1521-1527.
- ↑ Knapik M, Knapik P, Nadziakiewicz P, et al. Comparison of remifentanil or fentanyl administration during isoflurane anesthesia for coronary artery bypass surgery. Med Sci Monit. 2006;12(8):P133-P138
- ↑ De Baerdemaeker LEC, Jacobs S, Pattyn P, Mortier EP, Struys MMRF. Influence of intraoperative opioid on postoperative pain and pulmonary function after laparoscopic gastric banding: remifentanil TCI vs sufentanil TCI in morbid obesity. Br J Anaesth. 2007;99(3):404-411.
- ↑ Michelsen LG, Hug CC Jr. The pharmacokinetics of remifentanil. J Clin Anesth 1996;8:679–82
- ↑ Guy J, Hindman BJ, Baker KZ, et al. Comparison of remifentanil and fentanyl in patients undergoing craniotomy for supratentorial space-occupying lesions. Anesthesiology. 1997;86(3):514-524.
- ↑ Weale NK, Rogers CA, Cooper R, Nolan J, Wolf AR (February 2004). "Effect of remifentanil infusion rate on stress response to the pre-bypass phase of paediatric cardiac surgery". Br J Anaesth. 92 (2): 187–94. doi:10.1093/bja/aeh038. PMID 14722167.
- ↑ "Remifentanil Actavis" (in svenska). Archived from the original on 21 August 2014. Retrieved 21 Aug 2014.
- ↑ White, L. D.; Hodsdon, A.; An, G. H.; Thang, C.; Melhuish, T. M.; Vlok, R. (1 November 2019). "Induction opioids for caesarean section under general anaesthesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials". International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia. 40: 4–13. doi:10.1016/j.ijoa.2019.04.007. ISSN 0959-289X. PMID 31230994. Archived from the original on 28 August 2021. Retrieved 29 July 2021.
- ↑ Stocki, Daniel; Matot, Idit; Einav, Sharon; Eventov-Friedman, Smadar; Ginosar, Yehuda; Weiniger, Carolyn F. (Mar 2014). "A randomized controlled trial of the efficacy and respiratory effects of patient-controlled intravenous remifentanil analgesia and patient-controlled epidural analgesia in laboring women". Anesthesia and Analgesia. 118 (3): 589–97. doi:10.1213/ANE.0b013e3182a7cd1b. PMID 24149580. S2CID 4844447. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2021-07-29.
- ↑ Ulusoy H H (Feb 2014). "Sevoflurane/remifentanil versus propofol/remifentanil for electroconvulsive therapy: comparison of seizure duration and haemodynamic responses". J Int Med Res. 42 (1): 111–119. doi:10.1177/0300060513509036. PMID 24398757.
- 1 2 Patel SS, Spencer CM (Sep 1996). "Remifentanil". Drugs. 52 (3): 417–27. doi:10.2165/00003495-199652030-00009. PMID 8875131.
- ↑ Ternes, J. W., & O'Brien, C. P. (1990). The opioids: Abuse liability and treatments for dependence. Advances in alcohol & substance abuse, 9(1-2), 27-45.
- ↑ Panlilio, L. V., & Schindler, C. W. (2000). Self-administration of remifentanil, an ultra-short acting opioid, under continuous and progressive-ratio schedules of reinforcement in rats. Psychopharmacology, 150(1), 61-66.
- ↑ Baylon, G. J., Kaplan, H. L., Somer, G., Busto, U. E., & Sellers, E. M. (2000). Comparative abuse liability of intravenously administered remifentanil and fentanyl. Journal of clinical psychopharmacology, 20(6), 597-606.
- ↑ Levine, A. I., & Bryson, E. O. (2010). Intranasal self-administration of remifentanil as the foray into opioid abuse by an anesthesia resident. Anesthesia & Analgesia, 110(2), 524-525.
- ↑ Bodor, Nicholas; Buchwald, Peter (2000). "Soft drug design: General principles and recent applications". Medicinal Research Reviews. 20 (1): 58–101. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1098-1128(200001)20:1<58::AID-MED3>3.0.CO;2-X. PMID 10608921.
- ↑ Hoke JF, Cunningham F, James MK, Muir KT, Hoffman WE (April 1997). "Comparative pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of remifentanil, its principle metabolite (GR90291) and alfentanil in dogs". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 281 (1): 226–32. PMID 9103501.
- ↑ Dahaba, Ashraf A.; Grabner, Tanja; Rehak, Peter H.; List, Werner F.; Metzler, Helfried (2004-09-01). "Remifentanil versus Morphine Analgesia and Sedation for Mechanically Ventilated Critically Ill Patients". Anesthesiology. 101 (3): 640–646. doi:10.1097/00000542-200409000-00012. ISSN 0003-3022. PMID 15329588. S2CID 17192694. Archived from the original on 2021-05-25. Retrieved 2021-07-29.
- ↑ Spies, Claudia; MacGuill, Martin; Heymann, Anja; Ganea, Christina; Krahne, Daniel; Assman, Angelika; Kosiek, Heinrich-Rudolf; Scholtz, Kathrin; Wernecke, Klaus-Dieter; Martin, Jörg (March 2011). "A prospective, randomized, double-blind, multicenter study comparing remifentanil with fentanyl in mechanically ventilated patients". Intensive Care Medicine. 37 (3): 469–476. doi:10.1007/s00134-010-2100-5. ISSN 0342-4642. PMID 21165734. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2021-07-29.
- ↑ Feldman, P. L. (2006). Discovery and Development of the Ultrashort-acting Analgesic Remifentanil. Drug Discovery and Development, Drug Discovery, 1, 339.
- ↑ Gatlin, Larry Alan, Shirley Ann Heiman, and Janet Sue Lewis. "Stable formulations of remifentanil." U.S. Patent No. 5,866,591. 2 Feb. 1999.
- ↑ US Food and Drug Administration. (2010). Orange book: approved drug products with therapeutic equivalence evaluations. Silver Spring, MD: US FDA.
- ↑ "Remifentanil". Archived from the original on 2020-08-06. Retrieved 2021-07-29.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help)
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |
- "Remifentanil Hydrochloride". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Archived from the original on 2021-08-29. Retrieved 2021-07-29.