Fluorophen
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C22H26FNO |
| Molar mass | 339.454 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
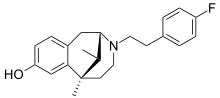
Fluorophen, or fluorofen, is a fluorinated analogue of phenazocine, an opioid drug of the benzomorphan group, which was developed as a radioligand for the purpose of labeling opioid receptors during PET scans (with 18F).[1][2] Unlike most other benzomorphan derivatives, fluorophen acts as a full agonist of the opioid receptors with preferential affinity for the μ-opioid receptor (approximately 6x that of morphine), similar but slightly lower affinity for the δ-opioid receptor (equipotent to [D-Ala2, D-Leu5]enkephalin), and very low affinity for the κ-opioid receptor.[1][2]
References
- 1 2 Rice KC, Konicki PE, Quirion R, Burke TR, Pert CB (November 1983). "Synthesis and pharmacological characterization of (+/-)-5,9 alpha-dimethyl-2-[2-(4-fluorophenyl)ethyl]-2'-hydroxy-6,7-benzomorphan (fluorophen), a ligand suitable for visualization of opiate receptors in vivo". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 26 (11): 1643–5. doi:10.1021/jm00365a017. PMID 6313921.
- 1 2 Cody Paul Coyne (9 January 2008). Comparative Diagnostic Pharmacology: Clinical and Research Applications in Living-System Models. John Wiley & Sons. p. 692. ISBN 978-0-470-34429-3. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.