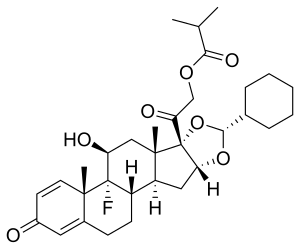
Ciclesonide
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Alvesco, Omnaris, Omniair, others |
| Other names | (11β, 16α)-16, 17-[[(R)-cyclohexylmethylene]bis(oxy)]-11-hydroxy-21- (2-methyl-1-oxopropoxy)- pregna-1, 4-diene-3, 20-dione |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Glucocorticoid[1] |
| Main uses | Asthma, allergic rhinitis[2][1] |
| Side effects | Inhaled: Headache, throat pain, upper respiratory infection, join pain, thrush, pneumonia[2] Nose spray: Nosebleeding, headache, ear pain, throat pain[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Inhalation, nose spray |
| Typical dose | 80 to 320 ucg OD to BID[3] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Inhaled: Monograph Nose: Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607008 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C32H44O7 |
| Molar mass | 540.697 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Ciclesonide, sold under the brand name Omnaris among others, is a medication used to treat asthma and allergic rhinitis.[2][1] For asthma it is inhaled while for rhinitis it is used as a nose spray.[2][1]
Common side effects when inhaled include headache, throat pain, upper respiratory infection, join pain, thrush, and pneumonia.[2] Common side effects when sprayed in the nose include nosebleeding, headache, ear pain, and throat pain.[1] Other side effects may include glaucoma and adrenal suppression.[4] Safety in pregnancy has not been well studied.[4] It is a corticosteroid, specifically a glucocorticoid.[2][1]
Ciclesonide was patented in 1990 and approved for medical use in 2005.[5] It was approved for use in the United States in 2006.[6] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines as an alternative to budesonide.[7] In the United Kingdom 120 doses of 160 microgram inhaler costs the NHS about £38 as of 2021.[3] This amount in the United States costs about 260 USD.[8]
Medical use
Dosage
The dose for asthma is generally 80 to 320 micrograms once to twice per day.[3]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Ciclesonide (EENT) Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 11 March 2016. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 "Ciclesonide (Systemic, Oral Inhalation) Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 27 January 2021. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- 1 2 3 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 278. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- 1 2 "DailyMed - ALVESCO- ciclesonide aerosol, metered". dailymed.nlm.nih.gov. Archived from the original on 17 April 2021. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ↑ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 488. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2021-03-21. Retrieved 2020-12-21.
- ↑ "FDA News Release. FDA Approves New Treatment for Allergies". Food and Drug Administration. 2006-10-23. Archived from the original on 2016-10-23. Retrieved 2009-07-30.
- ↑ World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ↑ "Alvesco Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
Further reading
- Rossi S, ed. (2006). Australian Medicines Handbook. Adelaide: Australian Medicines Handbook. ISBN 0-9757919-2-3.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|