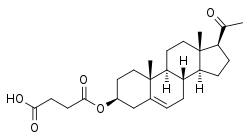
Pregnenolone succinate
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Panzalone, Formula 405 |
| Other names | Pregnenolone hemisuccinate; Pregn-5-en-3β-ol-20-one 3β-(hydrogen succinate) |
| Routes of administration | Topical |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.022.728 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C25H36O5 |
| Molar mass | 416.558 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Pregnenolone succinate (USAN; brand names Panzalone, Formula 405; also known as pregnenolone hemisuccinate or pregn-5-en-3β-ol-20-one 3β-(hydrogen succinate)) is a synthetic pregnane steroid and an ester of pregnenolone which is described as a glucocorticoid and anti-inflammatory drug and has been patented and marketed as a topical medication in the form of a cream for the treatment of allergic, pruritic, and inflammatory dermatitis.[1][2][3] It has also been described as a non-hormonal sterol, having neurosteroid activity, and forming a progesterone analogue via dehydrogenation.[4]
In addition to its glucocorticoid effects, pregnenolone succinate has been found to act as a negative allosteric modulator of the GABAA receptor and a positive allosteric modulator of the NMDA receptor similarly to pregnenolone sulfate.[5][6][7][8]
See also
References
- ↑ J. Elks (14 November 2014). The Dictionary of Drugs: Chemical Data: Chemical Data, Structures and Bibliographies. Springer. pp. 666–. ISBN 978-1-4757-2085-3.
- ↑ Martin Negwer; Hans-Georg Scharnow (4 October 2001). Organic-chemical drugs and their synonyms: (an international survey). Wiley-VCH. p. 2649. ISBN 978-3-527-30247-5.
3β-Hydroxypregn-5-en-20-one hydrogen succinate = (3β)-3-(3-Carboxy-1-oxo-propoxy)pregn-5-en-20-one. S: Formula 405. Panzalone. Pregnenolone succinate. U: Glucocorticoid (anti-inflammatory, anti-allergic).
- ↑ George W.A Milne (8 May 2018). Drugs: Synonyms and Properties: Synonyms and Properties. Taylor & Francis. pp. 1408–. ISBN 978-1-351-78989-9.
- ↑ Sheryl S. Smith (27 October 2003). Neurosteroid Effects in the Central Nervous System: The Role of the GABA-A Receptor. CRC Press. pp. 344, 356. ISBN 978-0-203-50816-9.
- ↑ Irwin RP, Lin SZ, Rogawski MA, Purdy RH, Paul SM (1994). "Steroid potentiation and inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated intracellular Ca++ responses: structure-activity studies". J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 271 (2): 677–82. PMID 7965782.
- ↑ Yaghoubi N, Malayev A, Russek SJ, Gibbs TT, Farb DH (1998). "Neurosteroid modulation of recombinant ionotropic glutamate receptors". Brain Res. 803 (1–2): 153–60. doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(98)00644-1. PMID 9729352. S2CID 41180982.
- ↑ Shirakawa H, Katsuki H, Kume T, Kaneko S, Ito J, Akaike A (2002). "Regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate cytotoxicity by neuroactive steroids in rat cortical neurons". Eur. J. Pharmacol. 454 (2–3): 165–75. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(02)02493-7. PMID 12421643.