Nizatidine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Axid, Tazac, others |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | H2 antagonist[1] |
| Main uses | Stomach ulcers, gastroesophageal reflux disease[1] |
| Side effects | Headache, dizziness[1] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | By mouth |
| Typical dose | 75 to 300 mg/day[1] |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a694030 |
| Legal | |
| License data |
|
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | >70% |
| Protein binding | 35% |
| Metabolism | Liver |
| Elimination half-life | 1–2 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney |
| Chemical and physical data | |
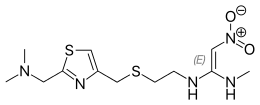
| Formula | C12H21N5O2S2 |
| Molar mass | 331.45 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Nizatidine, sold under the brand name Axid, is a medication used to treat stomach ulcers and gastroesophageal reflux disease.[1] It may be take for 4 to 12 weeks.[2] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Common side effects include headache and dizziness.[1] Other side effects may include pneumonia.[1] No harm has been found in pregnancy, but such use has not been well studied.[3] Use when breastfeeding appears safe.[2] It is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production.[1]
Nizatidine was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1987.[4] It was approved in the United States in 1988.[1] It is available as a generic medication and over the counter.[2] In the United Kingdom a month of medication costs the NHS about £18 as of 2021.[2] In the United States this costs about 20 USD.[5]
Medical use
Nizatidine is used to treat duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD/GORD), and to prevent stress ulcers.[6]
Dosage
It is used at a dose of 75 to 150 mg by mouth once or twice per day.[1]
Side effects
Side effects are uncommon, usually minor, and include diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, drowsiness, headache, and muscle aches.[6]
History
Nizatidine was developed by Eli Lilly, and was first marketed in the United States in 1988.[7] It is considered to be equipotent with ranitidine and differs by the substitution of a thiazole ring in place of the furan ring in ranitidine. In September 2000, Eli Lilly announced they would sell the sales and marketing rights for Axid to Reliant Pharmaceuticals.[8] Subsequently, Reliant developed the oral solution of Axid, marketing this in 2004, after gaining approval from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).[9] However, a year later, they sold rights of the Axid Oral Solution (including the issued patent[10] protecting the product) to Braintree Laboratories.[11]
Nizatidine proved to be the last new histamine H2 receptor antagonist introduced prior to the advent of proton pump inhibitors.
Axid (nizatidine) drug recalled due to presence of NDMA
See also
- Famotidine (Pepcid) — another H2 receptor antagonist
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 "Nizatidine Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 7 August 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 81. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- ↑ "Nizatidine Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 26 October 2020. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- ↑ Fischer J, Ganellin CR (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 44. ISBN 9783527607495. Archived from the original on 2020-07-29. Retrieved 2021-02-13.
- ↑ "Nizatidine Prices, Coupons & Savings Tips - GoodRx". GoodRx. Retrieved 13 November 2021.
- 1 2 "Nizatidine". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. NCBI Bookshelf. 25 January 2018. PMID 31643707. NBK548387. Archived from the original on 28 October 2021. Retrieved 19 March 2020.
- ↑ "Nizatidine: FDA-Approved Drugs". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). Archived from the original on 4 August 2020. Retrieved 20 March 2020.
- ↑ "Eli Lilly and Company and Reliant Pharmaceuticals Announce Agreement for U.S. Sales and Marketing Rights to Axid(R)". High Beam Encyclopedia. 7 September 2000. Archived from the original on May 26, 2008.
- ↑ "Reliant Pharmaceuticals to Launch AxidŽ Oral Solution". Reliant Pharmaceuticals, LLC. 26 July 2004. Archived from the original on 26 December 2013. Retrieved 13 February 2021.
- ↑ US 6930119, Bobotas G, Fawzy AA, "Liquid pharmaceutical composition", issued 24 June 2005, assigned to Reliant Pharmaceuticals, LLC
- ↑ "Reliant Pharmaceuticals Announces the Sale of Axid® Oral Solution to Braintree Laboratories". Reliant Pharmaceuticals, LLC. Archived from the original on August 14, 2007.
External links
| External sites: |
|
|---|---|
| Identifiers: |