Pirlindole
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Pirazidol |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 20–30% |
| Protein binding | 95% |
| Metabolism | hepatic |
| Onset of action | 2 to 8 hours |
| Elimination half-life | 2.1 hours [1] |
| Excretion | urine (50–70%), feces (25–45%) |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
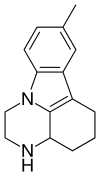
| Formula | C15H18N2 |
| Molar mass | 226.323 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
Pirlindole (Lifril, Pyrazidol) is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase A (RIMA) which was developed and is used in Russia as an antidepressant.[2]: 337 It is structurally and pharmacologically related to metralindole.
See also
References
- ↑ Pöldinger W (1985). "Pirlindole: results of an open clinical study in out-patients and of a double-blind study against maprotiline.". Psychiatry the State of the Art. Boston, MA.: Springer. pp. 283–289. doi:10.1007/978-1-4613-2363-1_44. ISBN 978-1-4613-2363-1.
- ↑ Medvedev AE, Shvedov VI, Chulkova TM, Fedotova OA, Saederup E, Squires RF (1998). Finberg JP, Youdim MB, Riederer P, Tipton KF (eds.). "The influence of the antidepressant pirlindole and its dehydro-derivative on the activity of monoamine oxidase A and GABAA receptor binding". Journal of Neural Transmission. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplement. 52 (Supplementum): 337–42. doi:10.1007/978-3-7091-6499-0_36. ISBN 978-3211830376. PMID 9564636.
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.