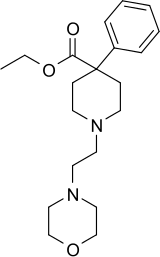
Morpheridine
Morpheridine (Morpholinoethylnorpethidine)[1] is a 4-phenylpiperidine derivative that is related to the clinically used opioid analgesic drug pethidine (meperidine). It is a strong analgesic with around 4 times the potency of pethidine,[2] and unlike pethidine, does not cause convulsions, although it produces the standard opioid side effects such as sedation and respiratory depression.[3]
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.749 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H30N2O3 |
| Molar mass | 346.471 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Morpheridine is not currently used in medicine and is a Schedule I drug which is controlled under UN drug conventions.[4]
Synthesis
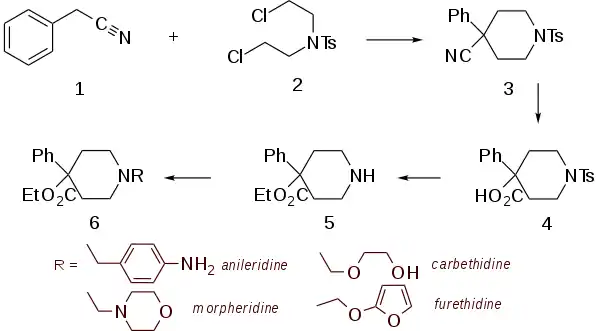
The key intermediate, normeperidine, is obtained by a scheme closely akin to the parent molecule. Thus, alkylation of benzyl cyanide (1) with the tosyl analog of the bischloroethylamine (2) leads to the substituted piperidine (3). Basic hydrolysis serves to convert the nitrile to the acid (4). Treatment of this last with sulfuric acid in ethanol serves both to esterify the acid and to remove the tosyl group to yield the secondary amine (5).
Alkylation of that amine by means of N-(2-chloroethyl)morpholine gives morpheridine.[6]
See also
References
- US 2795581, Stern ES, Anderson RJ, "Piperidine Compounds and Their Production", issued 06/11/1957, assigned to J.F. McFarlan & Co
- Holmes JM (February 1958). "Morpholinoethylnorpethidine hydrochloride in obstetrics". The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynaecology of the British Empire. 65 (1): 98–9. doi:10.1111/j.1471-0528.1958.tb06218.x. PMID 13514558. S2CID 1481693.
- Green AF, Ward NB (March 1956). "Analgesic and other properties of morpholinoethylnorpethidine". British Journal of Pharmacology and Chemotherapy. 11 (1): 32–4. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1956.tb01023.x. PMC 1509567. PMID 13304251.
- "Single convention on drugs 1961".
- Thorp RH, Walton E (May 1948). "Search for new analgesics; further homologues of pethidine and the pharmacology of these and other compounds". Journal of the Chemical Society. 2: 559–61. doi:10.1039/JR9480000559. PMID 18869425.
- Anderson RJ, Frearson PM, Stern ES (1956). "788. Some new analogues of pethidine. Part I". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 4088. doi:10.1039/JR9560004088.