Norpipanone
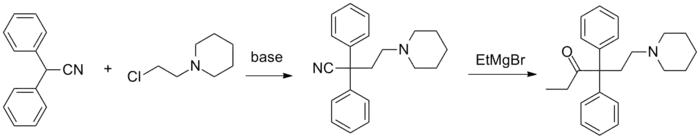
Norpipanone (INN, BAN; Hexalgon) is an opioid analgesic related to methadone which was developed in Germany and distributed in Hungary, Argentina, and other countries.[1][2] It had originally not been under international control but upon observation of case reports of addiction it was reviewed and shortly thereafter became a controlled substance.[1][2] In the United States, it is a Schedule I controlled substance (ACSCN 9636, zero annual manufacturing quota as of 2014). The salts in use are the hydrobromide (free base conversion ratio 0.806) and hydrochloride (0.902).
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Herchst 10495, NIH-7557 |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.383 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
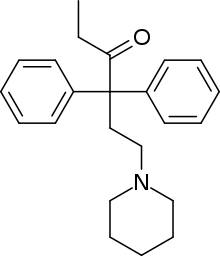
| Formula | C23H29NO |
| Molar mass | 335.491 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
- Dipipanone
- Normethadone
- Valeronitrile
References
- Buckingham JB (December 1995). Dictionary of Organic Compounds. CRC Press. p. 2883. ISBN 978-0-412-54090-5. Retrieved 11 May 2012.
- Patterson DS (12 March 2002). Foreign Relations of the United States, 1961-1963, Volume XXV: Organization of Foreign Policy; Information Policy; United Nations; Scientific Matters. Government Printing Office. pp. 766–767. ISBN 978-0-16-050885-1. Retrieved 11 May 2012.
- Duprè DJ, Elks J, Hems BA, Speyer KN, Evans RM (1949). "113. Analgesics. Part I. Esters and ketones derived from α-amino-ω-cyano-ωωdiarylalkanes". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed). Chemical Society: 500–510. doi:10.1039/JR9490000500.
- Bockmühl M, Ehrhart G (1949). "Über eine neue Klasse von spasmolytisch und analgetisch wirkenden Verbindungen, I". Justus Liebigs Annalen der Chemie. 561: 52–86. doi:10.1002/jlac.19495610107.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.