Zenazocine
Zenazocine (INN; WIN-42,964) is an opioid analgesic of the benzomorphan family which made it to phase II clinical trials before development was ultimately halted and it was never marketed.[1][2] It acts as a partial agonist of the μ- and δ-opioid receptors, with less intrinsic activity at the former receptor and more at the latter receptor (hence, it behaves more antagonistically at the former and more agonistically at the latter), and produces antinociceptive effects in animal studies.[1]
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
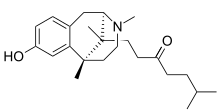
| Formula | C23H35NO2 |
| Molar mass | 357.538 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
References
- Ward SJ, Pierson AK, Michne WF (February 1985). "Pharmacological profiles of tonazocine (Win 42156) and zenazocine (Win 42964)". Neuropeptides. 5 (4–6): 375–8. doi:10.1016/0143-4179(85)90032-0. PMID 2860595. S2CID 20674308.
- Cotton R, James R (1985). "Chapter 3. Analgesics, Opioids and Opioid Receptors". In Bailey DM (ed.). Annual Reports in Medicinal Chemistry. Vol. 20. Academic Press. pp. 21–30. doi:10.1016/S0065-7743(08)61029-5. ISBN 978-0-12-040520-6.
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.