Ethylketazocine
Ethylketazocine (WIN-35,197-2), is an opioid drug of the benzomorphan family which has been used extensively in scientific research in the last few decades as a tool to aid in the study of the κ-opioid receptor.[1] However, due to its relatively poor selectivity for the κ-opioid receptor over the μ- and δ-opioid receptors (of which it has approximately 80% and 20% of the affinity for, respectively, in comparison), as well as its relatively poor intrinsic activity at all sites (i.e., acts as a partial agonist with mixed agonist and antagonist properties), it has been mostly replaced in recent times by newer and more potent and selective compounds like U-50,488 and ICI-199,441.[1][2][3]
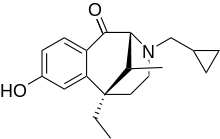 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ethylketocyclazocine |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 299.407 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
See also
- Benzomorphan
- Ketazocine
References
- Foye WO, Lemke TL (24 September 2007). Foye's Principles of Medicinal Chemistry. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 657. ISBN 978-0-7817-6879-5. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- London ED (1993). Imaging Drug Action in the Brain. CRC Press. p. 130. ISBN 978-0-8493-8843-9. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
- Freye E (3 April 2008). Opioids in Medicine: A Comprehensive Review on the Mode of Action and the Use of Analgesics in Different Clinical Pain States. Springer. p. 103. ISBN 978-1-4020-5946-9. Retrieved 22 April 2012.
Opioid receptor modulators | |
|---|---|
| MOR |
|
| DOR |
|
| KOR |
|
| NOP |
|
| Unsorted |
|
| Others |
|
Sigma receptor modulators | |
|---|---|
| σ1 |
|
| σ2 |
|
| Unsorted |
|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators | |
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.