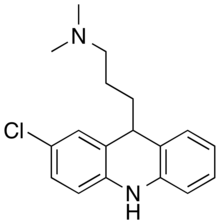
Clomacran
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Devryl, Olaxin,[1] Develar[2][3] |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C18H21ClN2 |
| Molar mass | 300.83 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.120 g/cm3 [1] |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Clomacran is an antipsychotic drug of the acridines class, developed in the 1970s[2] by the pharmaceutical company Smith, Kline & French under the brand names Devryl and Olaxin.[1]
It was withdrawn from the market in the UK, due to liver toxicity, in 1982.[5][6][7]
Synthesis
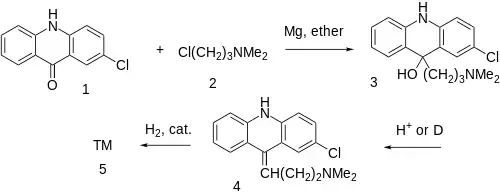
The first step involves FGI of 3-chloro-N,N-dimethylpropylamine Fb: [109-54-6] HCl: [5407-04-5] (2) into the Grignard reagent, i.e. magnesium;N,N-dimethylpropan-1-amine;chloride [19070-16-7] [154034-91-0]. The Grignard reaction with 2-chloroacridone [7497-52-1] (1) affords the tertiary carbinol (3). Dehydration by means of acid or simply heat gives the corresponding olefin (4). Catalytic reduction completes the synthesis of the tranquilizer, clomacran (5).
References
- 1 2 3 "Clomacran | 5310-55-4". ChemicalBook. Retrieved 2023-08-25.
- 1 2 Elks J, Ganellin CR, eds. (1990). Dictionary of Drugs. Boston, MA: Springer US. p. 297. doi:10.1007/978-1-4757-2085-3. ISBN 978-1-4757-2087-7.
- ↑ "Substâncias e remédios sob controle" [Substances and drugs under control] (PDF). Jornal do Brasil (in Brazilian Portuguese). 1986-11-05. p. 14. Archived (PDF) from the original on 2023-08-08. Retrieved 2023-08-08.
- ↑ Anvisa (2023-03-31). "RDC Nº 784 - Listas de Substâncias Entorpecentes, Psicotrópicas, Precursoras e Outras sob Controle Especial" [Collegiate Board Resolution No. 784 - Lists of Narcotic, Psychotropic, Precursor, and Other Substances under Special Control] (in Brazilian Portuguese). Diário Oficial da União (published 2023-04-04). Archived from the original on 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-08-03.
- 1 2 Dixit N, Patel C, Bhavsar M, Patel S, Rawal R, Solanki H (2022-05-02). "Quantitative Structure-activity Relationship (QSAR) study of Liver Toxic Drugs". International Association of Biologicals and Computational Digest. 1: 63–71. doi:10.56588/iabcd.v1i1.17. eISSN 2583-3995.
- ↑ "Clomacran". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 2023-08-25.
- ↑ Andrews EB, Moore N, eds. (2014). Mann's Pharmacovigilance (1st ed.). Wiley. doi:10.1002/9781118820186. ISBN 978-0-470-67104-7.
- ↑ Zirkle Charles L, U.S. Patent 3,131,190 (1964 to Smith Kline French Lab).
- ↑ E Anderson & H Graboyes, U.S. Patent 3,781,358 (1973 to SmithKline Beecham Corp).
- ↑ Elvin L Anderson & Harold Graboyes, U.S. Patent 3,692,834 (1972 to Smith Kline and French Laboratories Ltd, GlaxoSmithKline LLC SmithKline Beecham Corp).
- ↑ Elvin L Anderson & Harold Graboyes, U.S. Patent 3,919,312 (1975 to SmithKline Beecham Corp).
This article is issued from Offline. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.