Epirubicin
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Pronunciation | ep” i roo’ bi sin[1] |
| Trade names | Ellence, Pharmorubicin, Epirubicin Ebewe, others |
| Other names | Epirubicin hydrochloride |
IUPAC name
| |
| Clinical data | |
| Drug class | Anthracycline[1] |
| Main uses | Cancer[2] |
| Side effects | Hair loss, nausea, bone marrow suppression, inflammation of the mouth, hot flushes, diarrhea, infection, rash, fever[3] |
| WHO AWaRe | UnlinkedWikibase error: ⧼unlinkedwikibase-error-statements-entity-not-set⧽ |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of use | Intravenous |
| External links | |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a603003 |
| Legal | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetics | |
| Bioavailability | NA |
| Protein binding | 77% |
| Metabolism | Liver glucuronidation and oxidation |
| Excretion | Biliary and kidney |
| Chemical and physical data | |
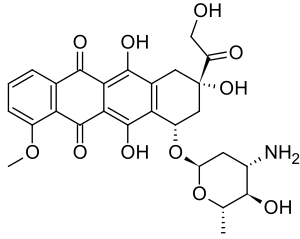
| Formula | C27H29NO11 |
| Molar mass | 543.525 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Epirubicin, sold under the brand name Ellence among others, is a medication used to treat breast cancer, stomach cancer, small cell lung cancer, ovarian cancer, colorectal cancer, lymphoma, bladder cancer, and leukemia.[3][2] It is given by injection into a vein or instilled in the bladder.[3][2]
Common side effects include hair loss, nausea, bone marrow suppression, inflammation of the mouth, hot flushes, diarrhea, infection, rash, and fever.[3] Other side effects may include heart damage, infertility, further cancers, and tumor lysis syndrome.[3] Use in pregnancy may harm the baby.[3] It is an anthracycline which is believed to work by intercalating DNA strands resulting in blocking DNA synthesis.[1]
Epirubicin was approved for medical use in the United States in 1999.[3] It is available as a generic medication.[2] In the United Kingdom 50 mg cost the NHS about £87 as of 2021.[2] This amount in the United States costs about 60 USD.[4]
Medical uses
Dosage
It is typically used at a dose of 60 to 100 mg per meter squared.[1]
Side effects
Anthracyclines (including Epirubicin) have been shown to have cardiotoxic properties.[5]
History
The first trial of epirubicin in humans was published in 1980.[6] Upjohn applied for approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in node-positive breast cancer in 1984, but was turned down because of lack of data.[7] In 1999 Pharmacia (who had by then merged with Upjohn) received FDA approval for the use of epirubicin as a component of adjuvant therapy in node-positive patients.
Patent protection for epirubicin expired in August 2007.
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Doxorubicin". LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012. Archived from the original on 16 May 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- 1 2 3 4 5 BNF 81: March-September 2021. BMJ Group and the Pharmaceutical Press. 2021. p. 947. ISBN 978-0857114105.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "EpiRUBicin Monograph for Professionals". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 7 June 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ↑ "Epirubicin Prices, Coupons & Patient Assistance Programs". Drugs.com. Archived from the original on 22 April 2021. Retrieved 15 December 2021.
- ↑ Mecinaj A, Gulati G, Heck SL, Holte E, Fagerland MW, Larsen AI, Blix ES, Geisler J, Wethal T, Omland T. Rationale and design of the PRevention of cArdiac Dysfunction during Adjuvant breast cancer therapy (PRADA II) trial: a randomized, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Cardiooncology. 2021 Sep 27;7(1):33. doi: 10.1186/s40959-021-00115-w. PMID: 34579775; PMCID: PMC8474901.
- ↑ Bonfante V, Bonadonna G, Villani F, Martini A (1980). "Preliminary clinical experience with 4-epidoxorubicin in advanced human neoplasia". Recent Results in Cancer Research. Fortschritte der Krebsforschung. Progres dans les Recherches Sur le Cancer. Recent Results in Cancer Research. 74: 192–9. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-81488-4_24. ISBN 978-3-642-81490-7. PMID 6934564.
- ↑ "Oncology Approval: epirubicin hydrochloride (Ellence)". On Target. Target Health Inc. September 15, 1999. Archived from the original on 2008-05-10. Retrieved 2007-08-04.
External links
| Identifiers: |
|---|